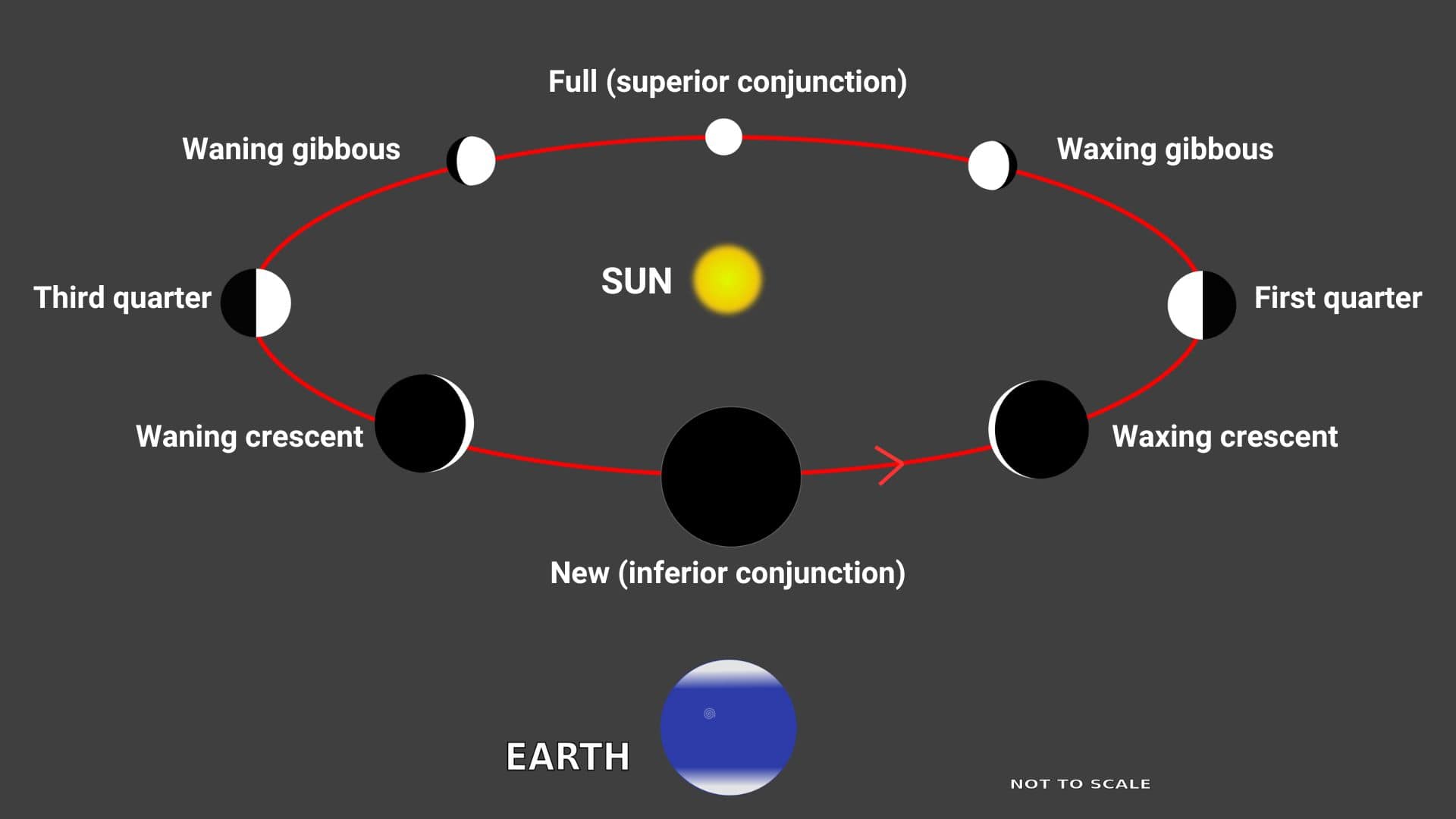
What is the moon phase today?
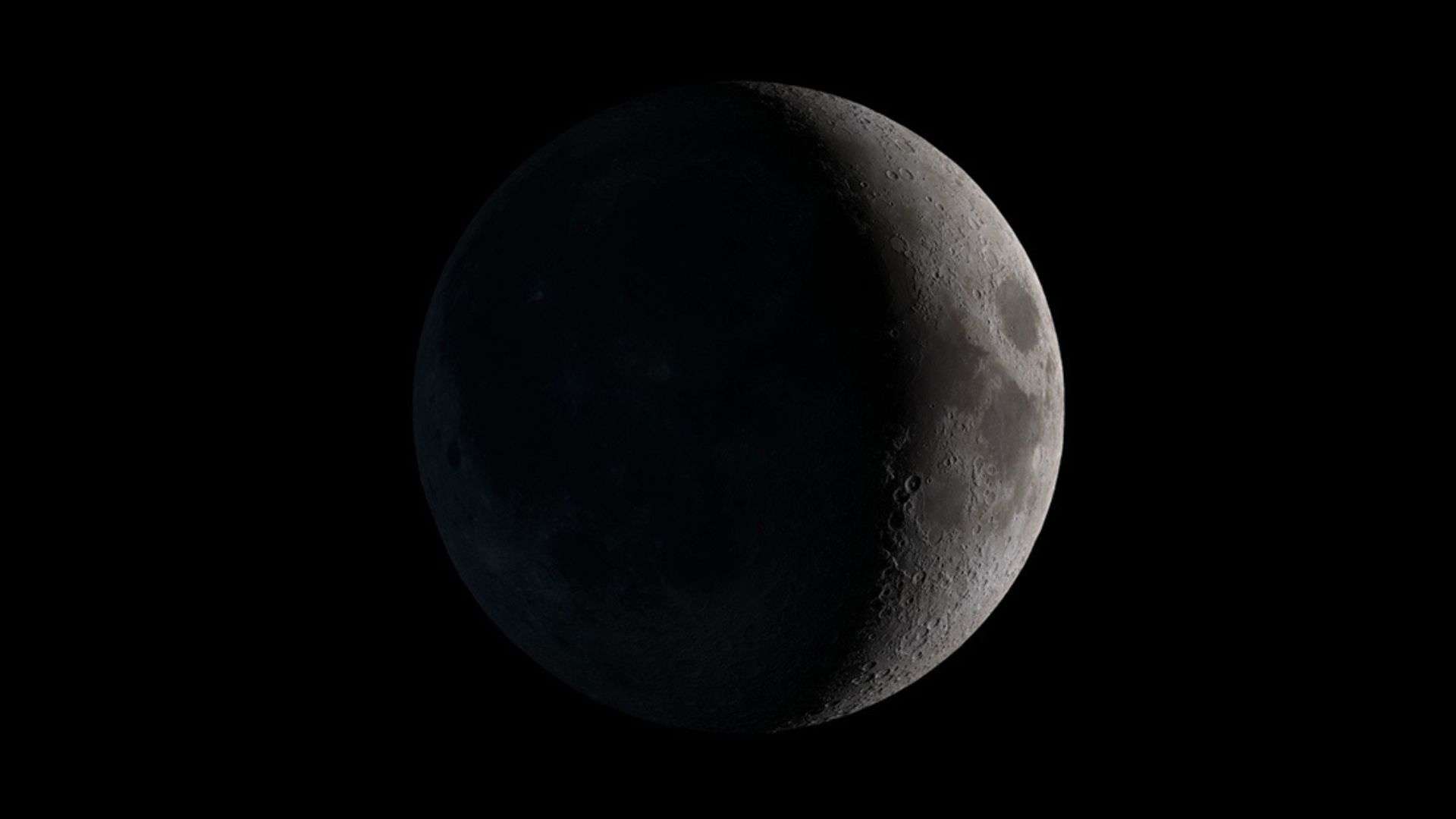
Today, on Friday, May 10, 2024, the moon is in the waxing crescent phase and is 2 days old. On this day, the moon is 8% illuminated, according to NASA. It is the second day after the new moon.
Waxing crescent: May 8 at 03:22 UTC to May 15 at 11:48 UTC

Phase: Second phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: Increases from 0.1% to 49.9%
Moon orientation: Right side of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and left side of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Secondary or intermediate
Rise time: Morning (between sunrise and noon) | Set time: Evening (between sunset and midnight)
Duration: Around 7 days. A waxing crescent moon starts right after the new moon and lasts until it becomes a first quarter moon.
Moon age: Greater than zero but less than a week.
When and where to see: Look west after sunset
Main article: All you need to know about the waxing crescent moon
First quarter (half moon): May 15 at 11:48 UTC
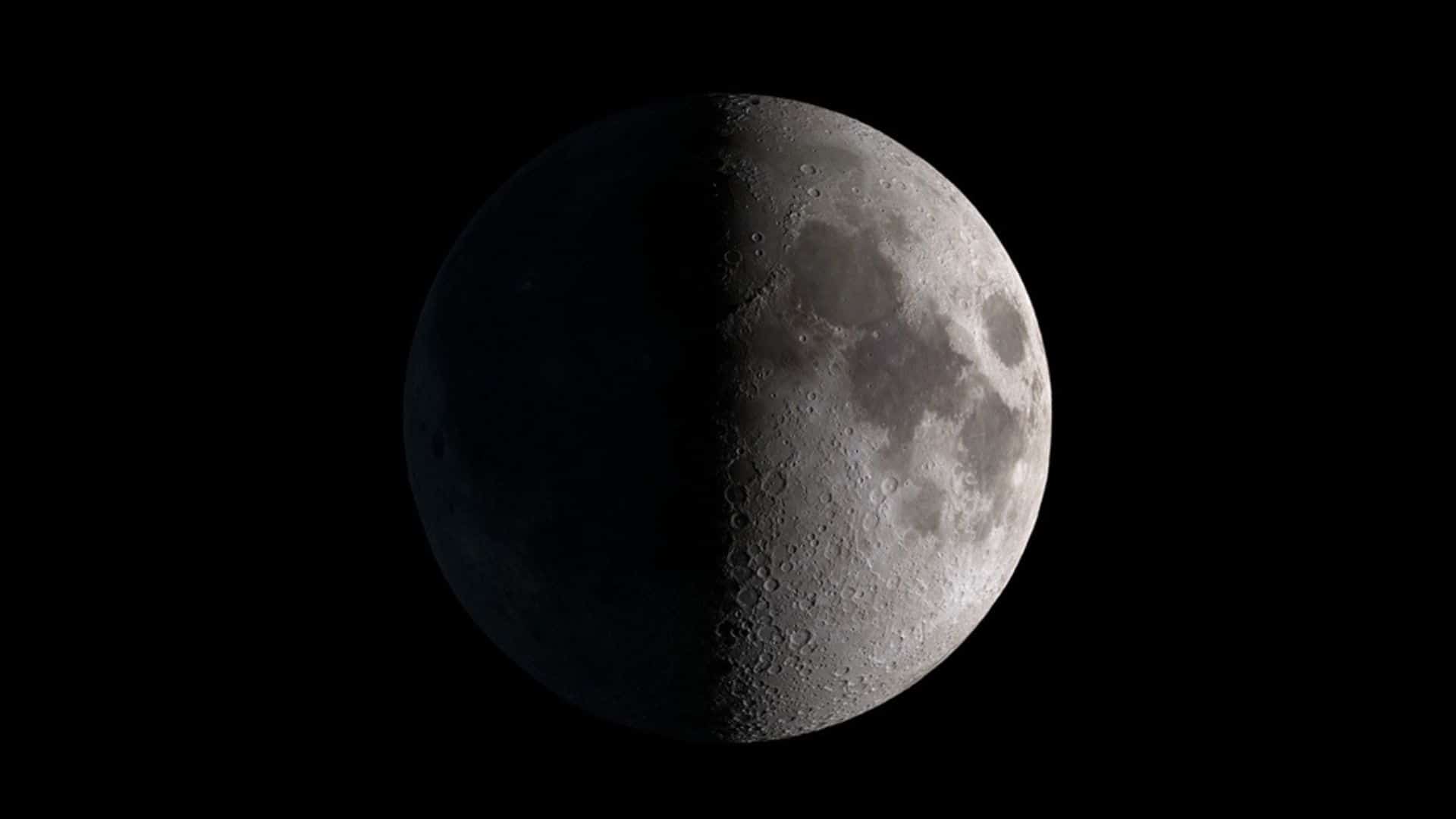

Phase: Third phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: 50%
Moon orientation: Right half of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and left half of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Primary
Rise time: Around noon | Set time: Around midnight
Duration: First quarter moon occurs at a precise moment in time.
Moon age: About a week
When and where to see: Look overhead in the early evening
Main article: All you need to know about the first quarter moon
Waxing gibbous: May 15 at 11:48 UTC to May 23 at 13:53 UTC
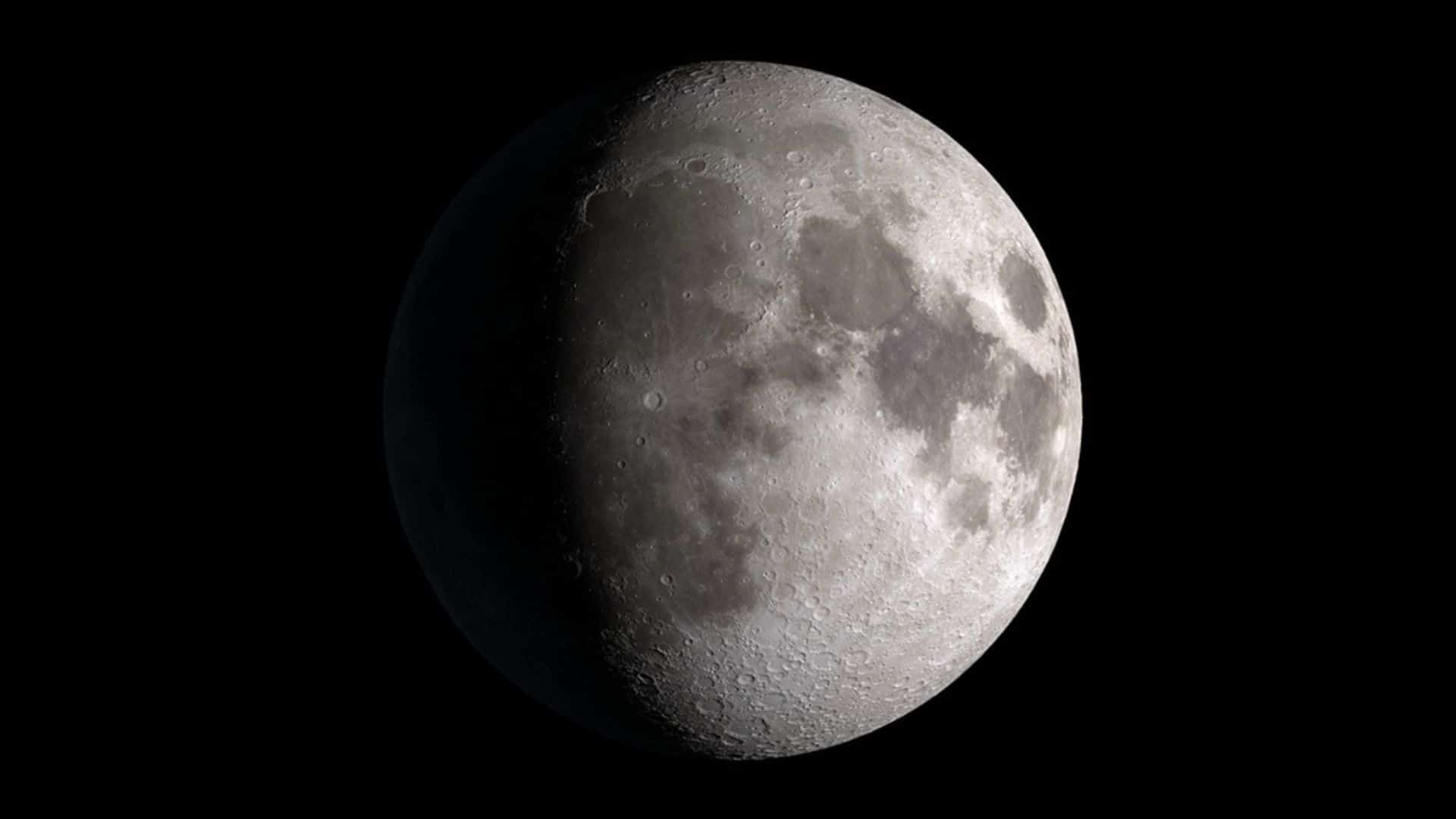

Phase: Fourth phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: Increases from 50.1% to 99.9%
Moon orientation: More than right half of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and more than left half of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Secondary or intermediate
Rise time: Afternoon (between noon and sunset) | Set time: After midnight (between midnight and sunrise)
Duration: Around 7 days. A waxing gibbous moon starts right after the first quarter moon and lasts until it becomes a full moon.
Moon age: Greater than a week but less than two weeks.
When and where to see: Look east in the early evening and west after midnight
Main article: All you need to know about the waxing gibbous moon
Full moon: May 23 at 13:53 UTC
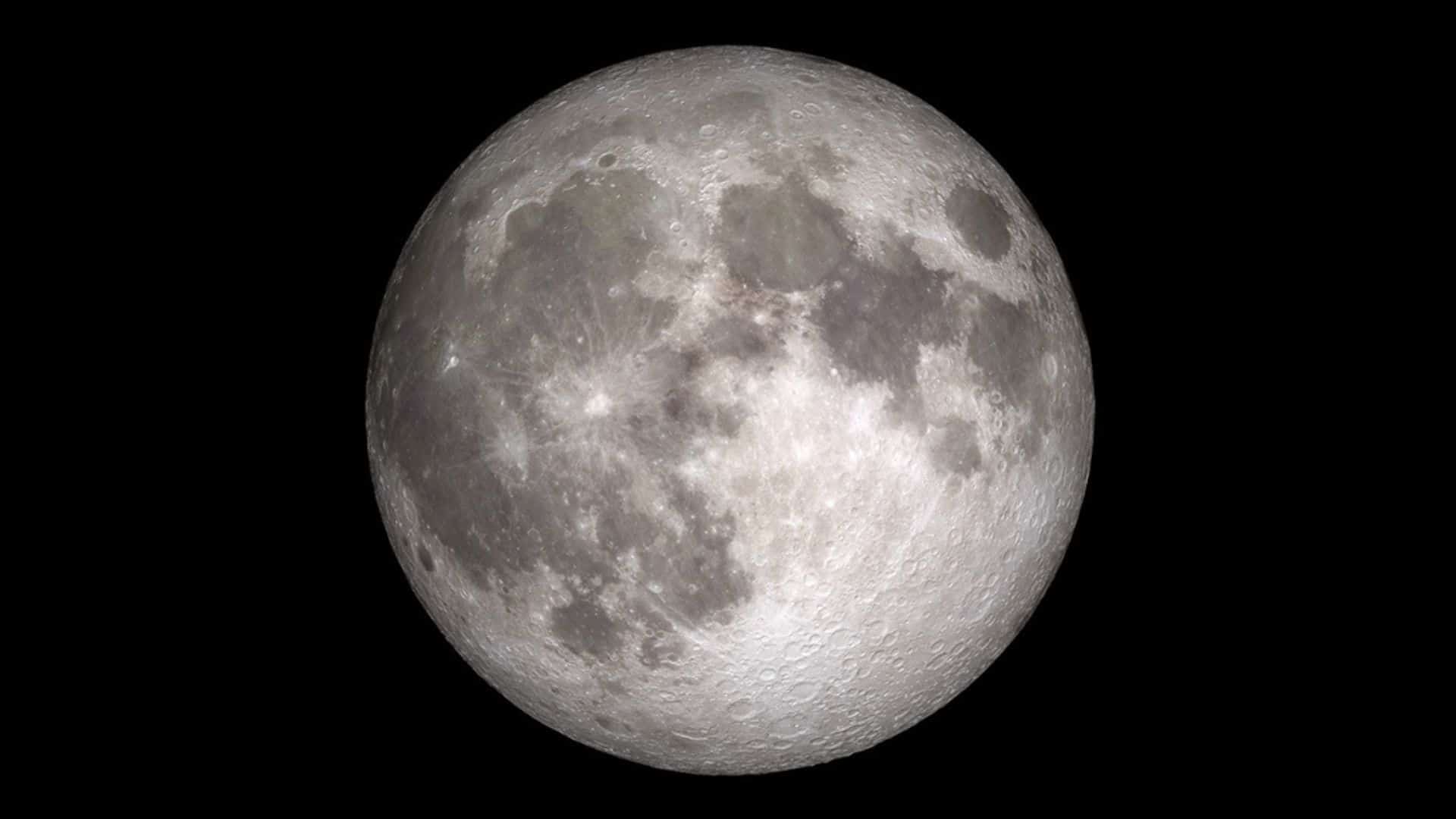

Phase: Fifth phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: 100%
Phase type: Primary
Rise time: Around sunset | Set time: Around sunrise
Duration: Full moon occurs at a precise moment in time.
Moon age: About two weeks
When and where to see: Look east in the early evening (after sunset), overhead around midnight and west in the early morning (before sunrise)
Main article: All you need to know about the full moon
Waning gibbous: May 23 at 13:53 UTC to May 30 at 17:13 UTC
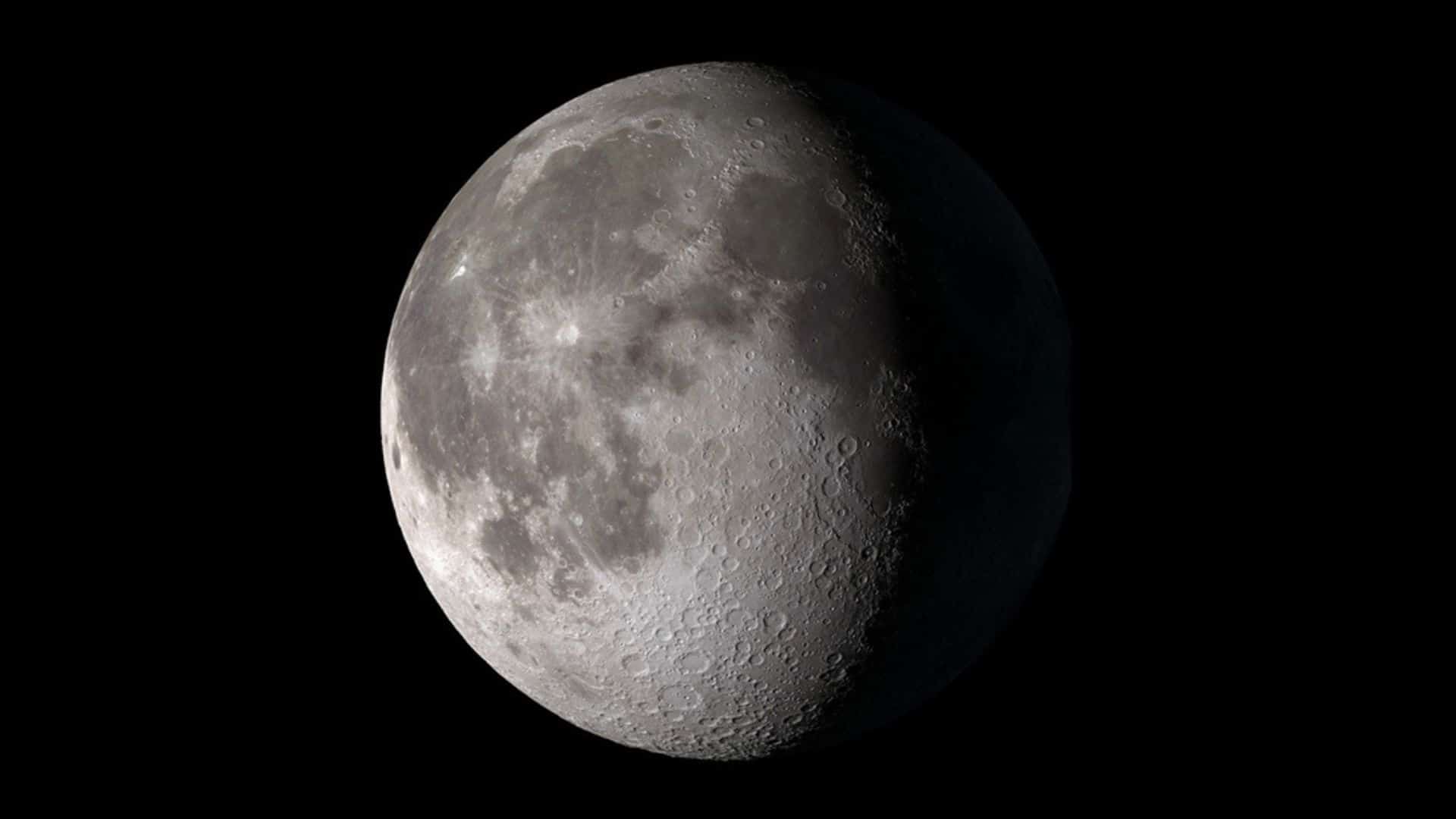

Phase: Sixth phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: Decreases from 99.9% to 50.1%.
Moon orientation: More than left half of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and more than right half of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Secondary or intermediate
Rise time: Evening (between sunset and midnight) | Set time: Morning (between sunrise and noon)
Duration: Around 7 days. A waning gibbous moon starts right after the full moon and lasts until it becomes a third quarter moon.
Moon age: Greater than two weeks but less than three weeks.
When and where to see: Look east in the late evening and west in the early morning
Main article: All you need to know about the waning gibbous moon
Third quarter (half moon): May 30 at 17:13 UTC
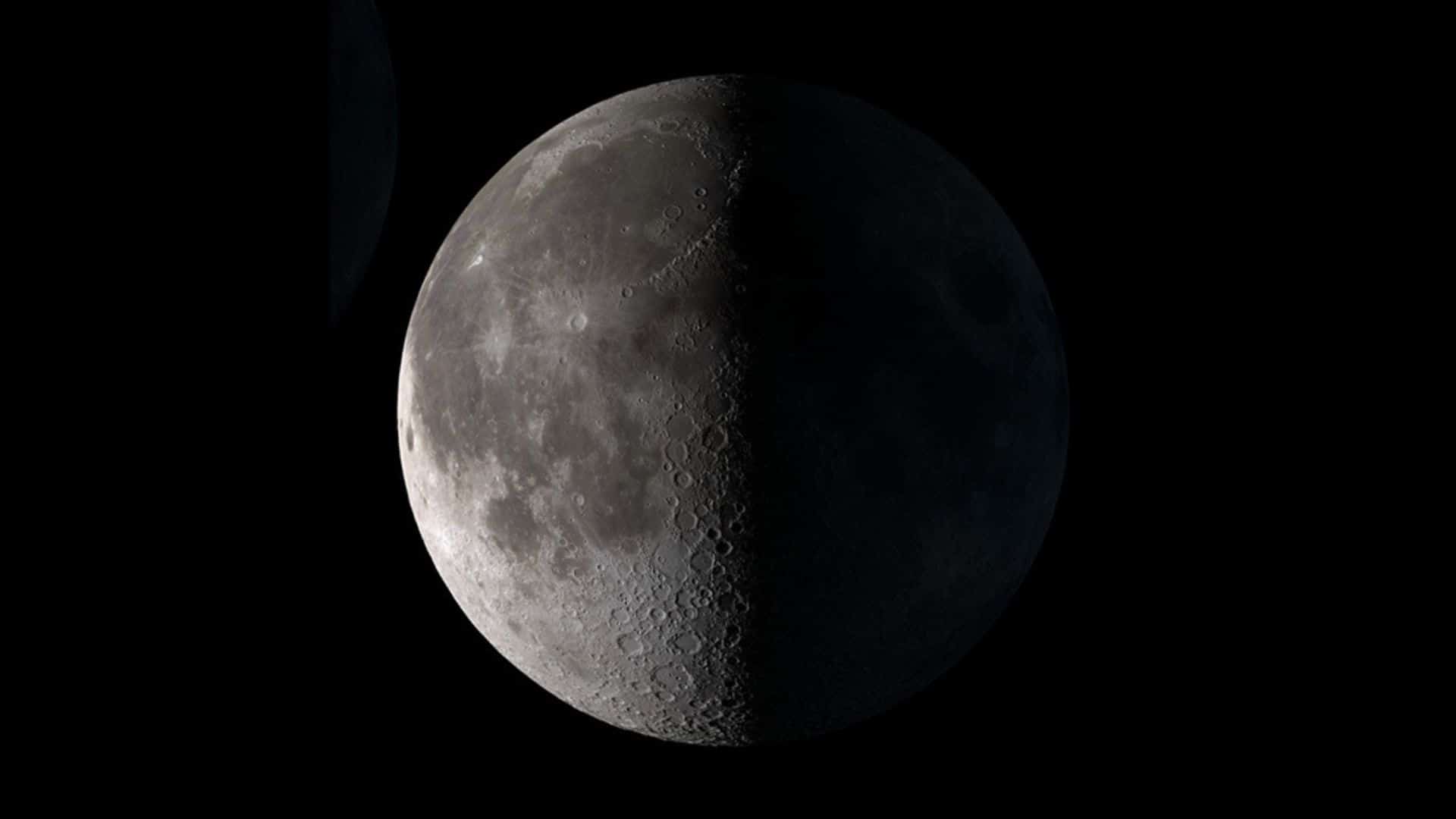

Phase: Seventh phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: 50%
Moon orientation: Left half of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and right half of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Primary
Rise time: Around midnight | Set time: Around noon
Duration: Third quarter moon occurs at a precise moment in time.
Moon age: About three weeks
When and where to see: Look overhead in the early morning
Main article: All you need to know about the third quarter moon
Waning crescent: May 30 at 17:13 UTC to June 6 at 12:38 UTC
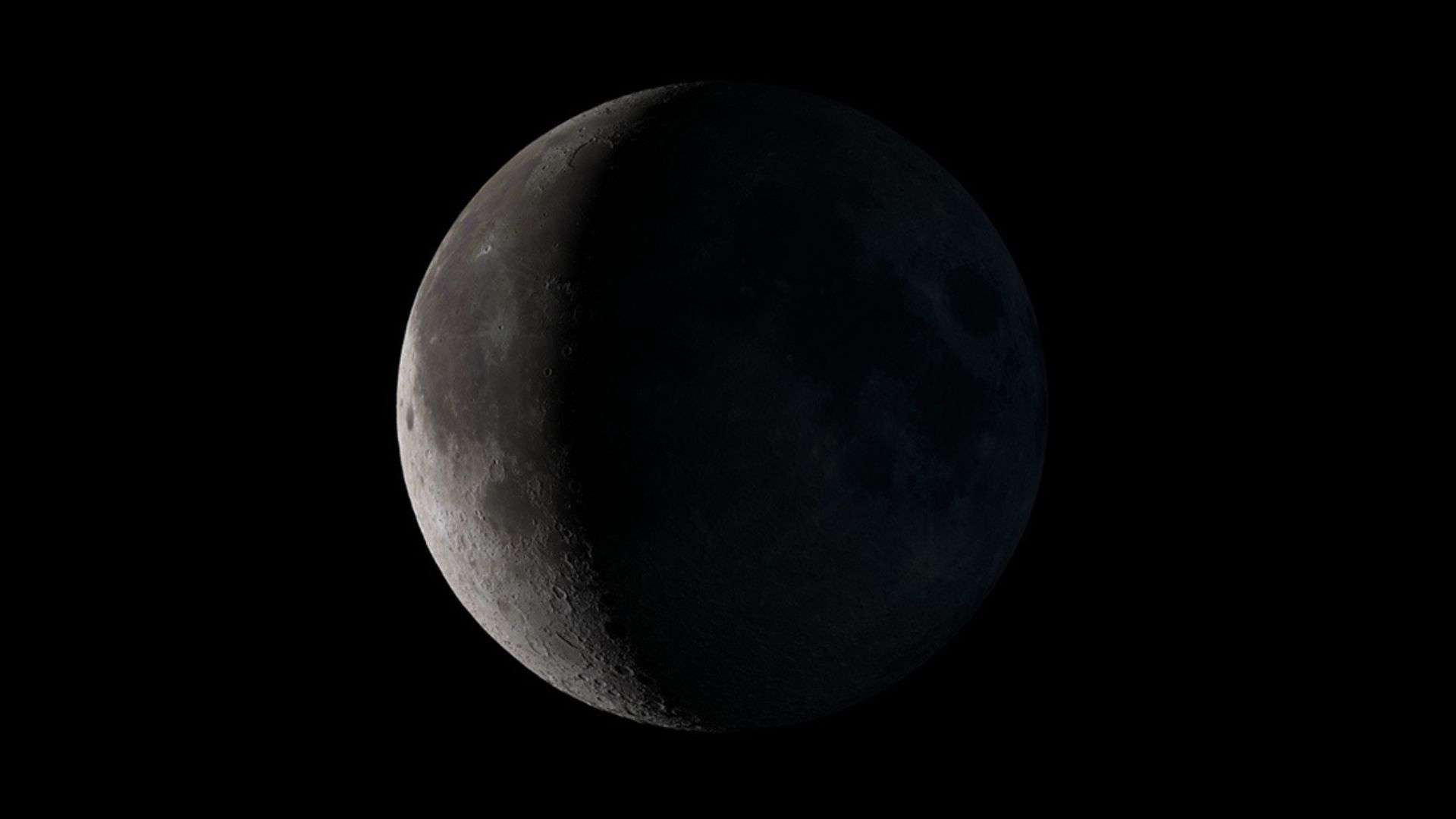

Phase: Eighth phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: Decreases from 49.9% to 0.1%.
Moon orientation: Left side of the moon is illuminated in the Northern Hemisphere and right side of the moon is illuminated in the Southern Hemisphere.
Phase type: Secondary or intermediate
Rise time: After midnight (between midnight and sunrise) | Set time: Afternoon (between noon and sunset)
Duration: Around 7 days. A waning crescent moon starts right after the third quarter moon and lasts until it becomes a new moon.
Moon age: Greater than three weeks but less than four weeks
When and where to see: Look east before sunrise
Main article: All you need to know about the waning crescent moon
New moon: June 6 at 12:38 UTC
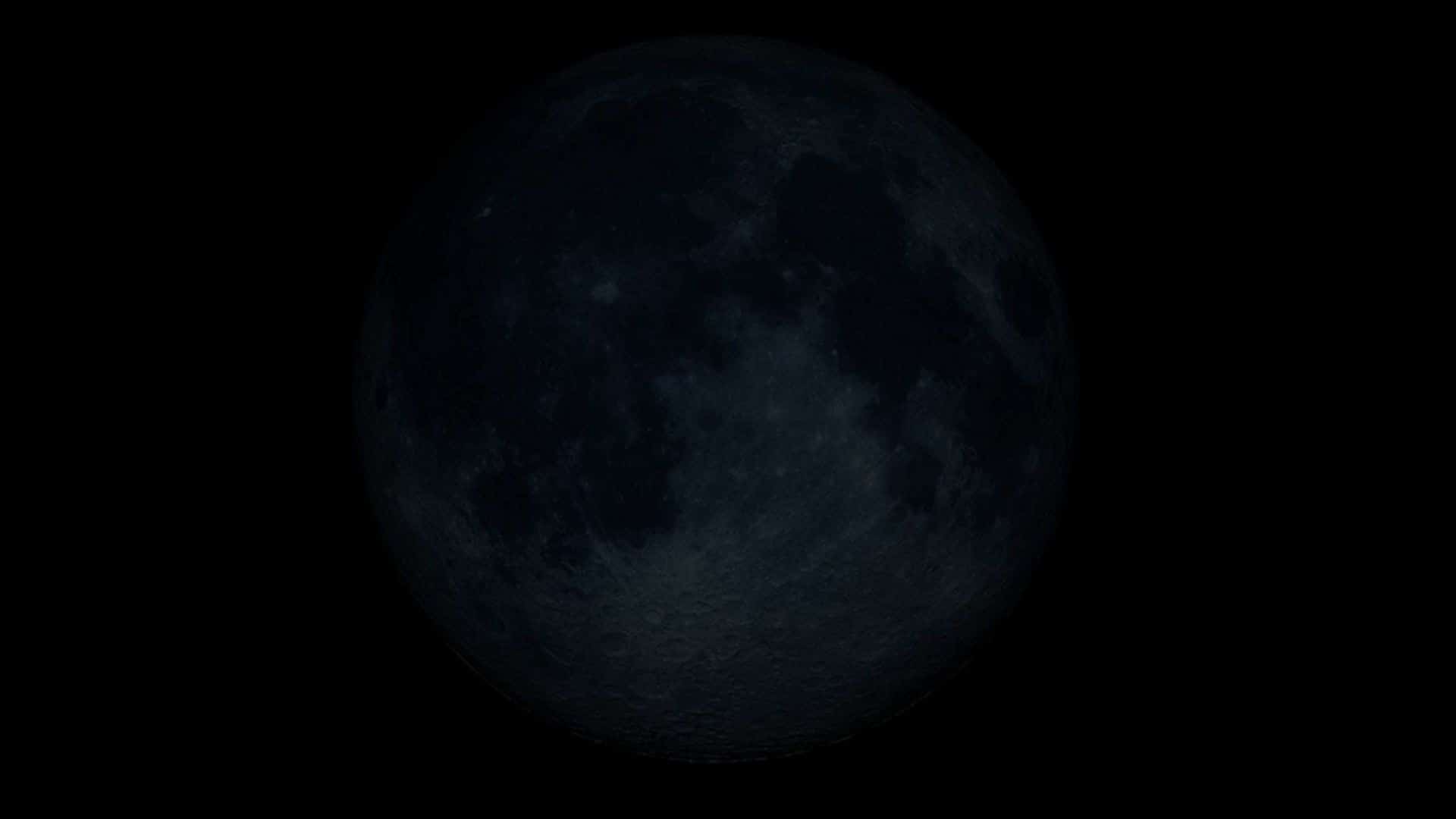

Phase: First phase of the lunar cycle out of eight phases.
Illuminated area: 0%
Phase type: Primary
Rise time: Around sunrise | Set time: Around sunset
Duration: New moon occurs at a precise moment in time.
Moon age: Zero
When and where to see: The invisible phase of the moon. A new moon is only visible during a solar eclipse.
Main article: All you need to know about the new moon
Understanding the phases of the moon
The moon doesn’t have its own light. The sun illuminates the moon’s surface. So the moonlight we see is actually reflected sunlight.
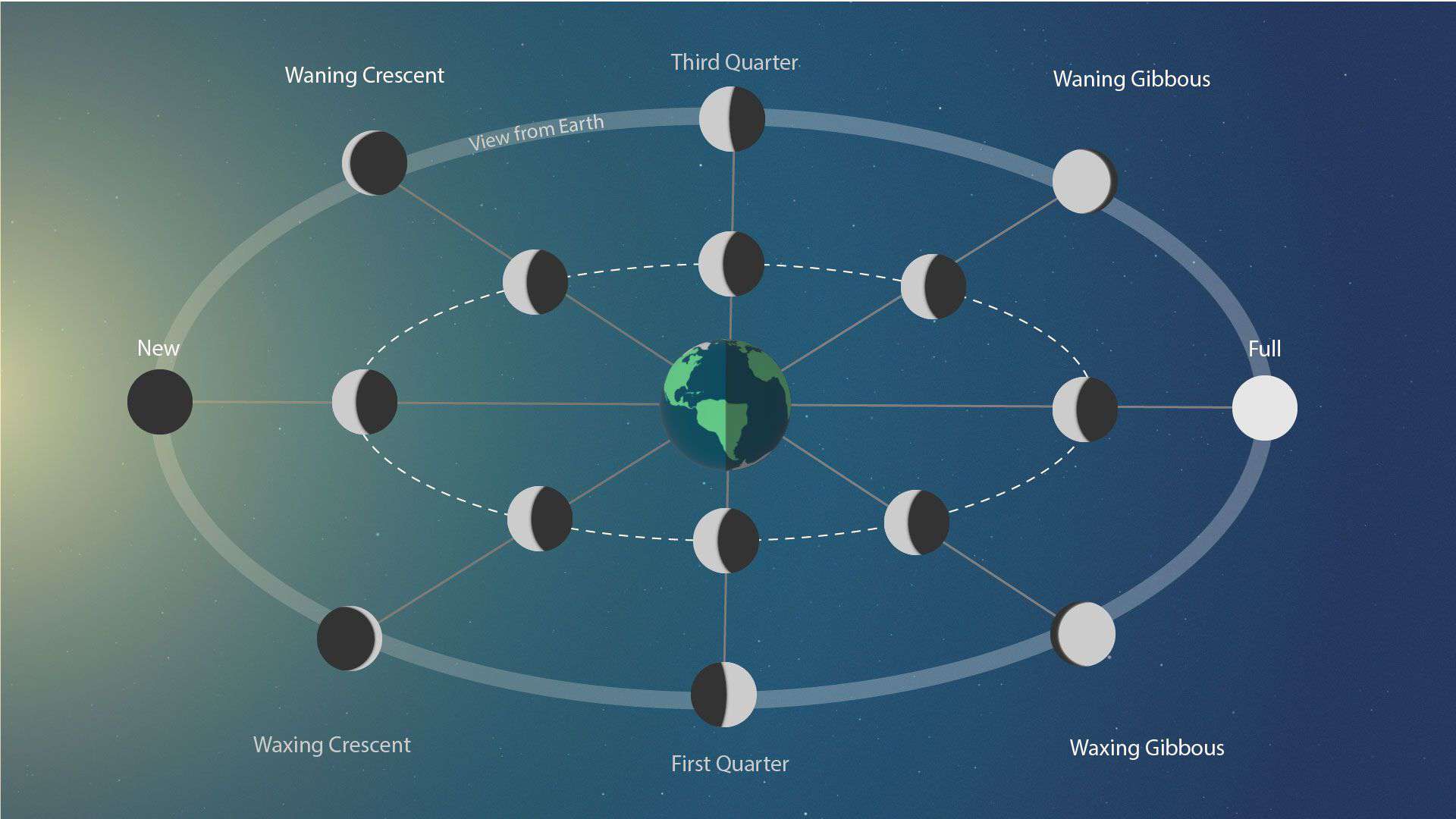
The sun always illuminates one hemisphere of the moon, as the moon is a globe. So for the sun, it is always a full moon.
However, for the earth, it’s not always a full moon. We see different illuminated portions of the moon, i.e., different phases of the moon, as it orbits the earth.
The moon takes 29.531 days to orbit the earth with respect to the sun. This is called a lunar cycle. In a lunar cycle, the moon goes through the following phases in order: new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent.
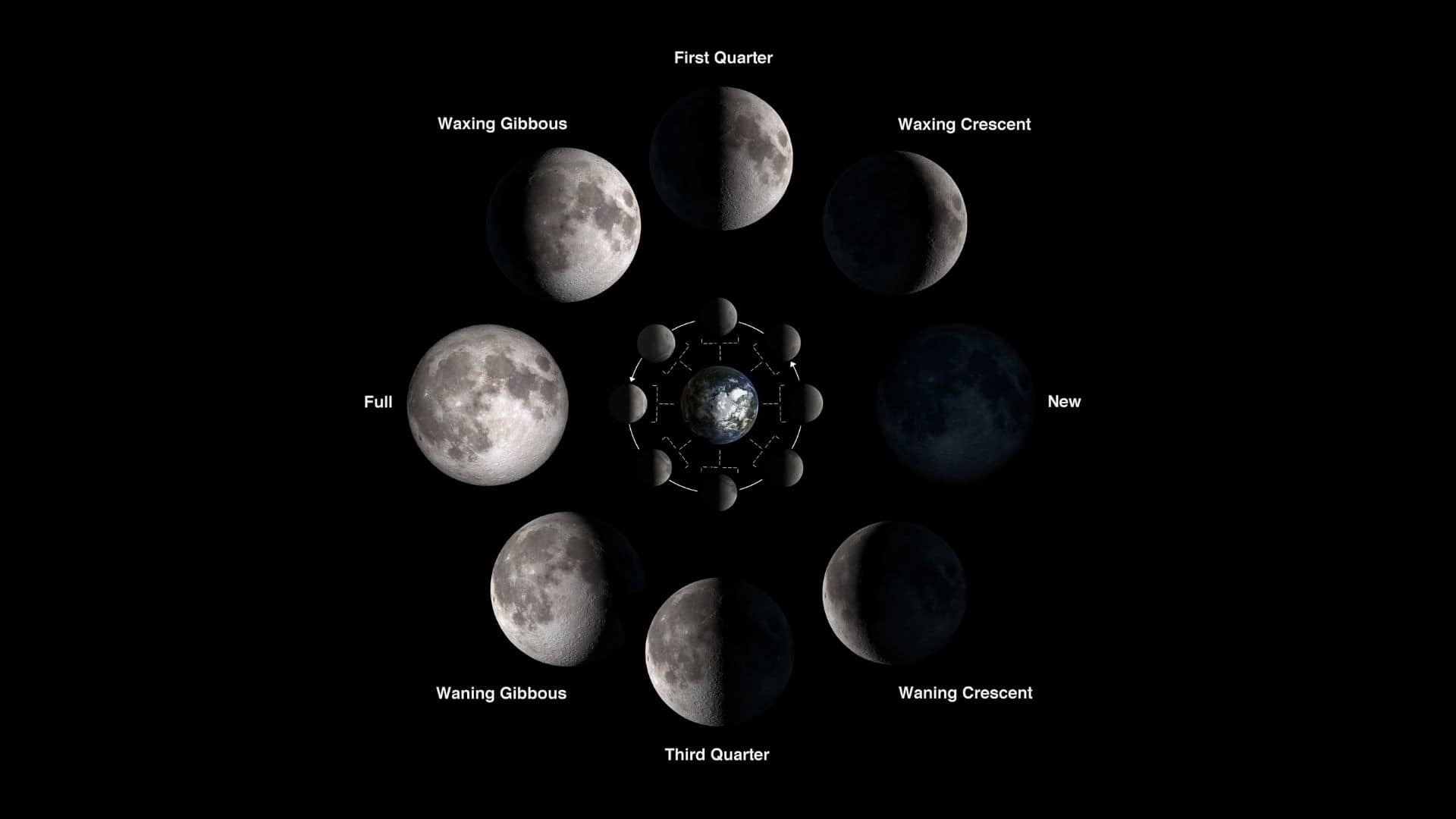

New moon: A new moon occurs when the moon is in inferior conjunction with the sun, i.e., it moves in front of the sun with respect to us. It is the invisible phase of the moon, as the side of the moon that faces us gets no light from the sun.
Waxing crescent: After a new moon, we see the first visible phase of the moon, called the waxing crescent. During a waxing crescent moon, the illuminated area of the moon grows day after day until it becomes a first quarter moon.
First quarter: About one week after the new moon, we see a half-illuminated moon in the sky. However, we call it a first quarter moon as it moves exactly one quarter area in its orbit around the earth.
Waxing gibbous: After the first quarter moon, the illuminated area of the moon continues to grow until it becomes a full moon. During this time, more than a half-illuminated area of the moon is seen in the sky, and we call it the waxing gibbous moon.
Full moon: About two weeks after the new moon, we see one hemisphere (full disk) of the moon, called a full moon. During this time, the moon is in opposition with the sun, i.e., it moves on the opposite side of the sun with respect to us, and we see the entire side of the moon that faces us.
Waning gibbous: After a full moon, the illuminated area of the moon shrinks day after day until it becomes a third quarter moon, called a waning gibbous moon.
Third quarter: About three weeks after the new moon or about one week after the full moon, we see another half-illuminated moon (opposite half compared to the first quarter) in the sky. However, we call it a third quarter moon, as it moves exactly three-quarters of its orbit around the earth at this time.
Waning crescent: After the third quarter moon, the illuminated area of the moon continues to shrink until it becomes a new moon again, called a waning crescent moon.
Moon phases calendar in 2024
Here are the dates and times (in UTC) of all the moon phases in 2024, according to NASA:
| New moon | First quarter | Full moon | Third quarter |
|---|---|---|---|
| — | — | — | January 4, 03:30 |
| January 11, 11:57 | January 18, 03:53 | January 25, 17:54 | February 2, 23:18 |
| February 9, 22:59 | February 16, 15:01 | February 24, 12:30 | March 3, 15:24 |
| March 10, 09:00 | March 17, 04:11 | March 25, 07:00 | April 2, 03:15 |
| April 8, 18:21 | April 15, 19:13 | April 23, 23:49 | May 1, 11:27 |
| May 8, 03:22 | May 15, 11:48 | May 23, 13:53 | May 30, 17:13 |
| June 6, 12:38 | June 14, 05:18 | June 22, 01:08 | June 28, 21:53 |
| July 5, 22:57 | July 13, 22:49 | July 21, 10:17 | July 28, 02:51 |
| August 4, 11:13 | August 12, 15:19 | August 19, 18:26 | August 26, 09:26 |
| September 3, 01:55 | September 11, 06:06 | September 18, 02:34 | September 24, 18:50 |
| October 2, 18:49 | October 10, 18:55 | October 17, 11:26 | October 24, 08:03 |
| November 1, 12:47 | November 9, 05:56 | November 15, 21:29 | November 23, 01:28 |
| December 1, 06:21 | December 8, 15:27 | December 15, 09:02 | December 22, 22:18 |
| December 30, 22:27 | — | — | — |
Please bookmark Spaceandtelescope.com or follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.