What is the phase of Mercury today?
Today, on May 20, 2024, Mercury is in the waxing gibbous phase and is 59% illuminated.
Waxing gibbous: May 15 to June 14
The waxing gibbous phase of Mercury begins on May 15, 2024, and ends on June 14, 2024.
Illuminated area: Increase from 50% to 100%
Disk size: Decrease from 7.4 arc-seconds to 5.1 arc-seconds
Phase angle: Decreases from 90° to 0° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises before sunrise and sets before sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the eastern sky preceding sunrise. It is harder to observe Mercury as the day goes on.
Full Mercury: June 14
The full phase of Mercury falls on June 14, 2024.
Illuminated area: 100%
Disk size: 5.1 arc-seconds
Phase angle: 0° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises and sets with the sun.
Visibility: Mercury is not visible as it disappears in the sun’s glare behind the sun.
Waning gibbous: June 14 to July 19
The waning gibbous phase of Mercury begins on June 14, 2024, and ends on July 19, 2024.
Illuminated area: Decrease from 100% to 50%
Disk size: Increase from 5.1 arc-seconds to 7.4 arc-seconds
Phase angle: Increase from 0° to 90° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises after sunrise and sets after sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the western sky following sunset. It is easier to observe Mercury as the day goes on.
Third quarter (half Mercury): July 19
The third quarter phase of Mercury falls on July 19, 2024.
Illuminated area: 50%
Disk size: 7.4 arc-seconds
Phase angle: 90° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises after sunrise and sets after sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the western sky following sunset.
Waning crescent: July 19 to August 19
The waning crescent phase of Mercury begins on July 19, 2024, and ends on August 19, 2024.
Illuminated area: Decrease from 50% to 0%
Disk size: Increase from 7.4 arc-seconds to 10.9 arc-seconds
Phase angle: Increase from 90° to 180° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises after sunrise and sets after sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the western sky following sunset. It is harder to observe Mercury as the day goes on.
New Mercury: August 19
The new phase of Mercury falls on August 19, 2024.
Illuminated area: 0%
Disk size: 10.9 arc-seconds
Phase angle: 180° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises and sets with the sun.
Visibility: Mercury is not visible as it disappears in the sun’s glare in front of the sun.
Waxing crescent: August 19 to September 6
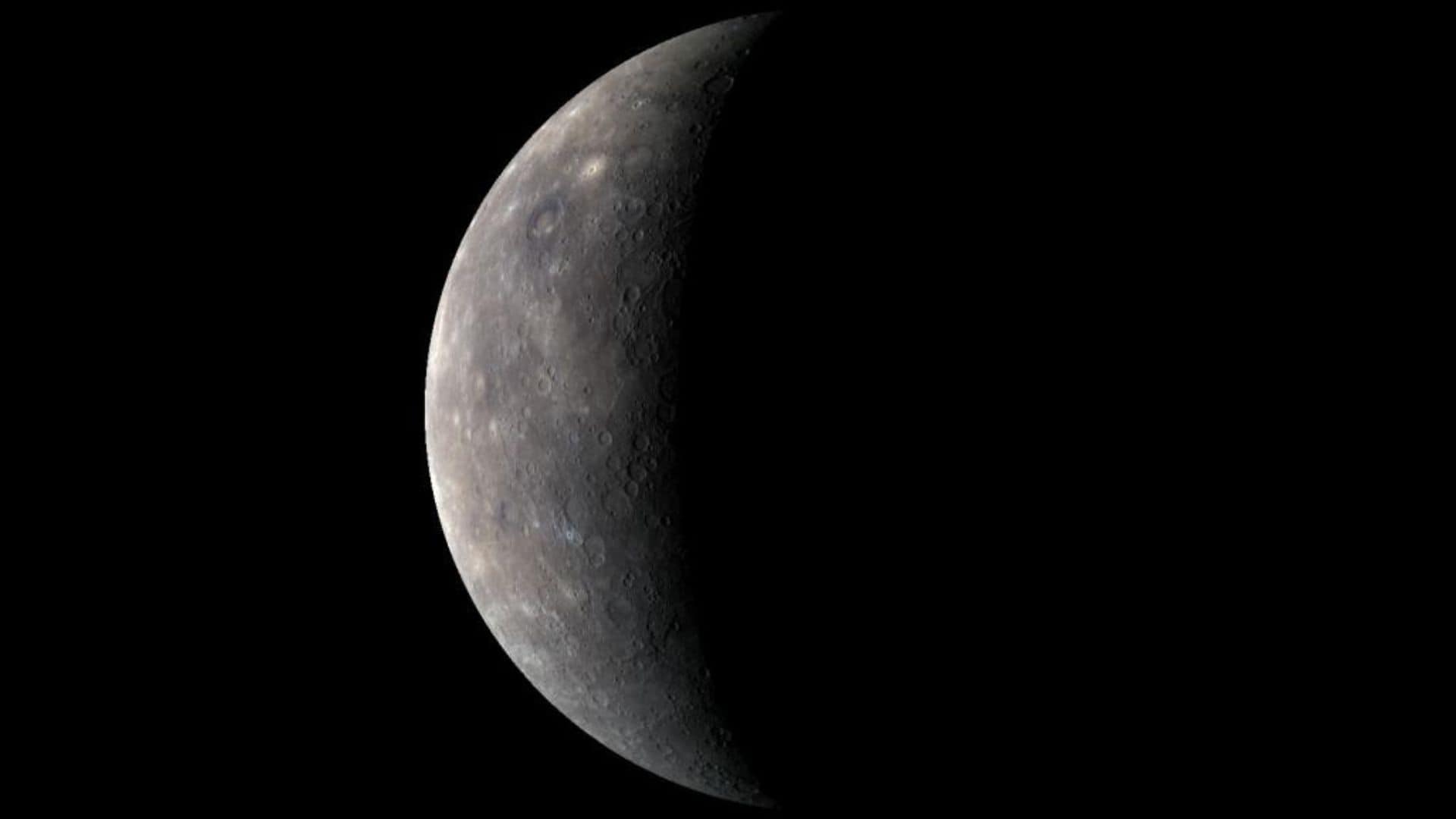

The waxing crescent phase of Mercury begins on August 19, 2024 and ends on September 6, 2024.
Illuminated area: Increases from 0% to 50%
Disk size: Decreases from 10.9 arc-seconds to 7.1 arc-seconds
Phase angle: Decreases from 180° to 90° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises before sunrise and sets before sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the eastern sky preceding sunrise. It is easier to observe Mercury as the day goes on.
First quarter (half Mercury): September 6
The first quarter phase of Mercury falls on September 6, 2024.
Illuminated area: 50%
Disk size: 7.1 arc-seconds
Phase angle: 90° (the angle between the sun, Mercury, and the earth).
Rise and set time: Mercury rises before sunrise and sets before sunset.
Visibility: Mercury is visible in the eastern sky preceding sunrise.
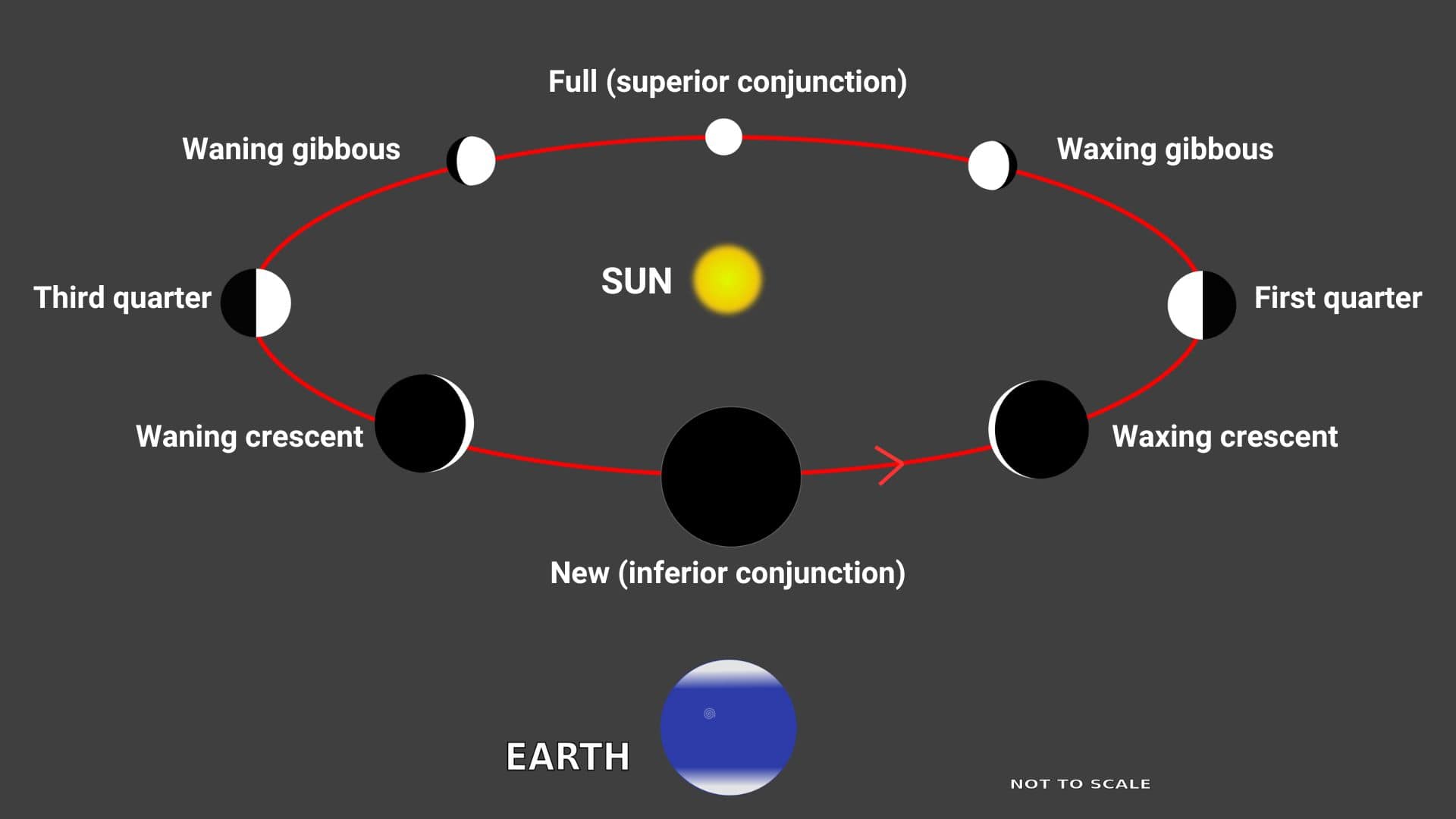
Understanding the phases of Mercury
If you look through a telescope from the earth, you will see that Mercury exhibits a full range of phases as it orbits the sun.
Mercury’s orbit is closer to the sun than Earth’s orbit. So it passes between the sun and the earth as it orbits the sun. That’s why Mercury exhibits a full range of phases.
Like the moon, Mercury also exhibits a total of eight phases. In order, these phases are: new Mercury, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full Mercury, waning gibbous, third quarter, and waning crescent.
However, there is one major difference between the phases of the moon and the phases of Mercury.
As the moon orbits around the earth, we see almost the same disk size of the moon throughout its phases. However, we don’t see the same disk size of Mercury throughout its phases from the earth as it orbits around the sun.
New Mercury: Mercury is in its new phase when it passes between the sun and the earth in its orbit, called the inferior conjunction of Mercury. During this time, Mercury is almost invisible, dimmest, and largest in size.
Mercury is almost invisible because it disappears in the sun’s glare in front of the sun on our sky’s dome, dimmest because the side of Mercury that faces our Earth is in complete darkness, and largest because it is closest to our Earth.
Waxing crescent: Mercury is in its waxing crescent phase when it recedes from Earth after the inferior conjunction position. During this time, the illuminated area of Mercury increases and its disk size decreases until it becomes a first quarter Mercury.
First quarter: Mercury is in its first quarter phase when it is one quarter away from the inferior conjunction position in its orbit. During this time, Mercury is 50% illuminated (half-illuminated).
Waxing gibbous: Mercury is in its waxing gibbous phase when it continues to recede from Earth after its first quarter phase. During this time, the illuminated area of Mercury continues to increase, and its disk size continues to decrease until it becomes a full Mercury.
Full Mercury: Mercury is in its full phase when it is located on the opposite side of the sun with respect to the earth in its orbit, called the superior conjunction of Mercury. During this time, Mercury is almost invisible, brightest, and smallest in size.
Mercury is almost invisible because it disappears in the sun’s glare behind the sun on our sky’s dome, brightest because the side of Mercury that faces our Earth is fully illuminated, and smallest because it is farthest from our Earth.
Waning gibbous: Mercury is in its waning gibbous phase when it approaches the earth after the superior conjunction position. During this time, the illuminated area of Mercury decreases and its disk size increases until it becomes a third quarter Mercury.
Third quarter: Mercury is in its third quarter phase when it is three-quarters away from the inferior conjunction position in its orbit. During this time, Mercury is 50% illuminated (half-illuminated).
Waning crescent: Mercury is in its waning crescent phase when it continues to approach the earth after its third quarter phase. During this time, the illuminated area of Mercury continues to decrease, and its disk size continues to increase until it becomes a new Mercury.
Mercury takes about 88 days to orbit the sun with respect to the background stars, called the sidereal period of Mercury. However, Mercury takes about 116 days to orbit the sun with respect to the earth, as the earth is also moving in its orbit, called the synodic period of Mercury. So Mercury takes about 116 days to complete a phase cycle, i.e., to go from its one “new” phase to the next “new” phase.
Please bookmark Spaceandtelescope.com or follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.



