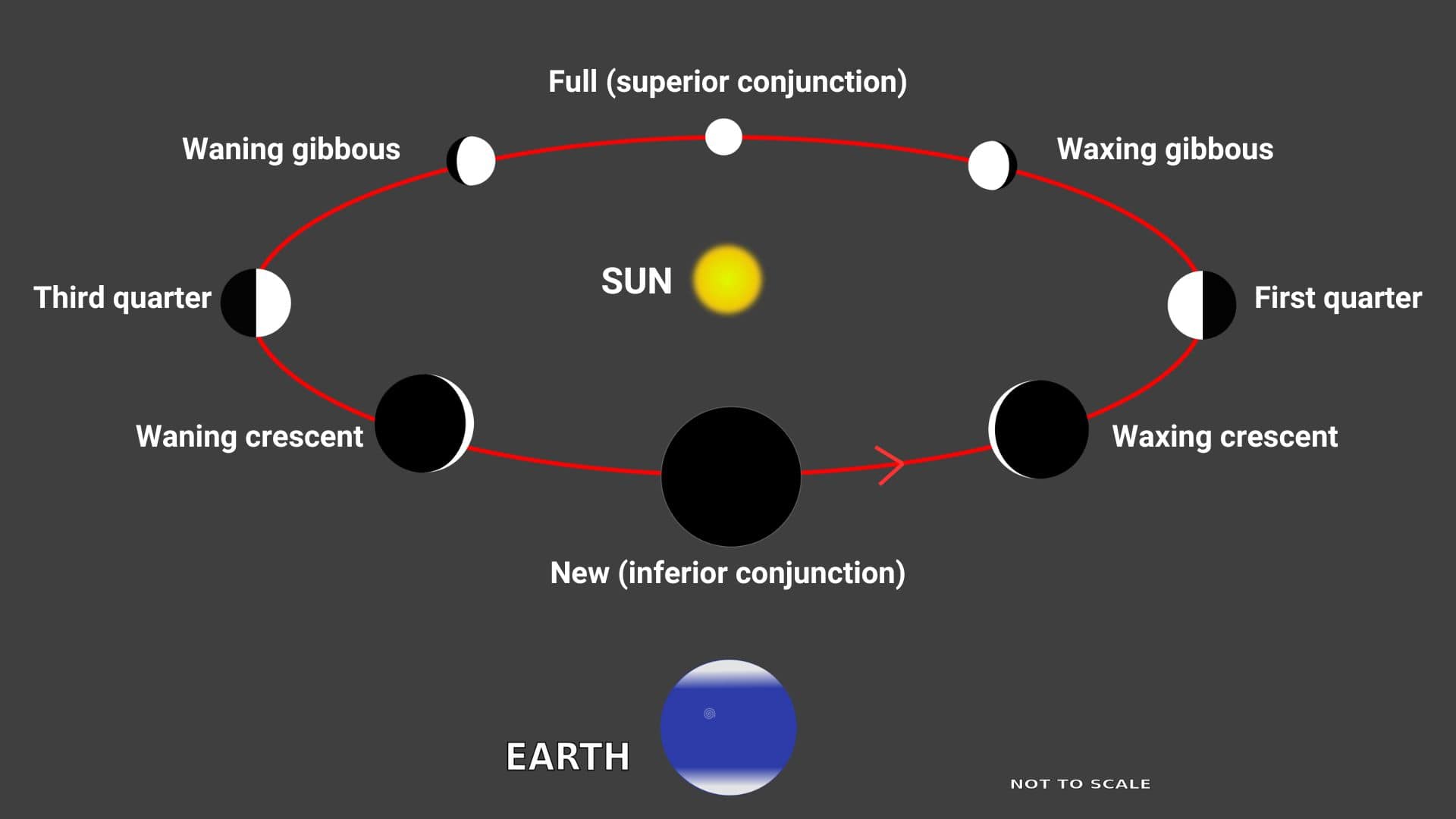
A full moon is when the sun, earth, and moon are aligned and the earth is positioned between the sun and moon. So during a full moon, the moon is located on the opposite side of the sun with respect to the earth.
The meaning of a full moon

It is called a full moon because the entire disk of the moon that faces Earth is fully illuminated.
Rise and set time of a full moon
A full moon rises in the east around the time of sunset, reaches its highest point (overhead point) in the sky around midnight and sets in the west around the time of sunrise.
During a full moon, the moon is on the opposite side of the Sun relative to the Earth. That’s why a full moon rises in the east when the sun sets in the west and the full moon sets in the west when the sun rises in the east.
Fifth phase of the lunar cycle
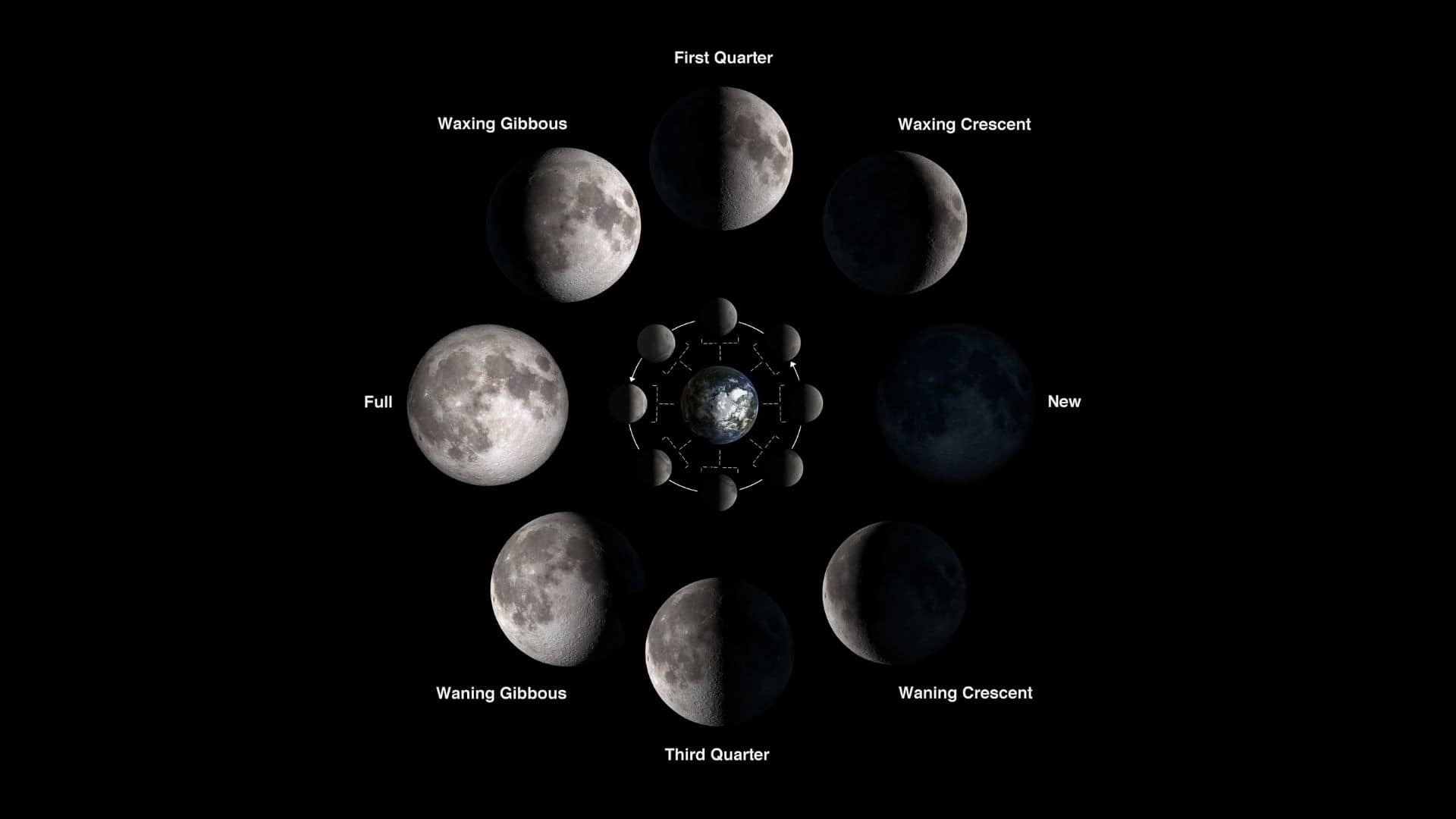

A lunar cycle starts with the new moon phase and goes through the new moon, waxing crescent moon, first quarter moon, waxing gibbous moon, full moon, waning gibbous moon, third quarter moon, waning crescent moon, and again back to the new moon.
So from the above lunar cycle, you see that the full moon is the fifth phase of the lunar cycle.
Second quarter moon
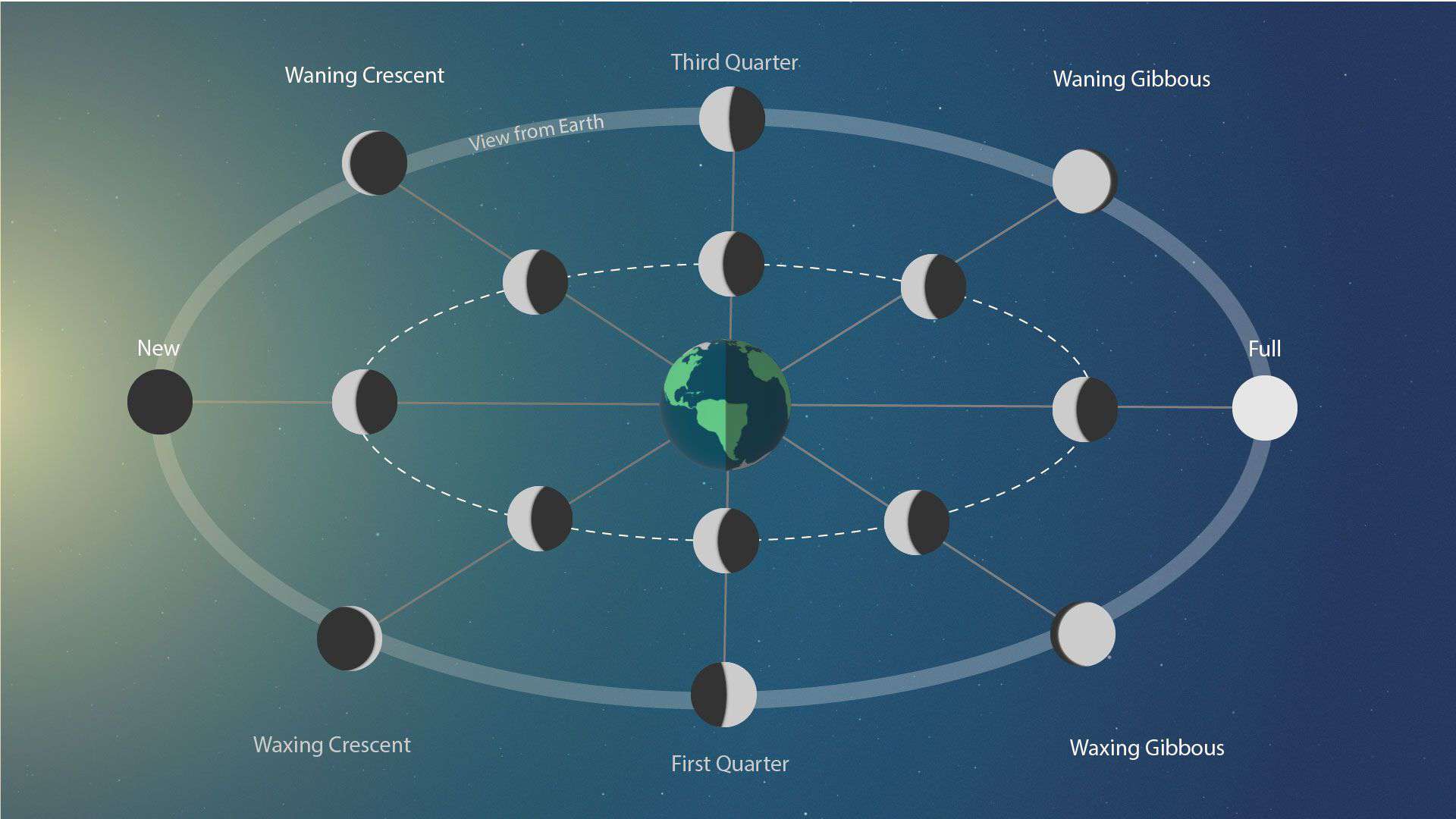
A full moon is also called a second quarter moon because a full moon occurs when the moon travels exactly two quarter area or 2/4 area or 180° area out of 360 degrees in its orbit around the Earth.
We measure a two quarter area or 180° area from the position of a new moon (when the moon is located in front of the sun with respect to the earth).
Duration of a full moon
A full moon occurs at a precise moment when the moon travels exactly two quarter area in its orbit around the earth. As a full moon occurs at a precise moment in time that’s why it has no duration.
However, a full moon looks full around 3 days in our naked eye. It’s the day of the full moon, before the day of the full moon, and after the day of the full moon.
A full moon occurs once every 29.531 days
The moon takes 29.531 days in its orbit to go from one full moon to the next full moon. This is called a synodic month.
So a full moon occurs once every synodic month or 29.531 days.
The age of a full moon is about 14 days
A lunar cycle starts with the new moon phase, and a full moon is seen in the sky about two weeks after the new moon. So the age of a full moon is about 14 days.
Second full moon in a calendar month is called a Blue Moon
As a full moon occurs once every 29.531 days so it’s possible to fit two full moons in a calendar month.
When you see two full moons in a calendar month then the second full moon of that month is called a Blue Moon.
For that to happen, the first full moon must be on the 1st or 2nd of a calendar month so that the second full moon is on the 30th or 31st.
The full moon at perigee is a Supermoon
When a full moon occurs at perigee, the closest point from the earth in its orbit, then it’s called a Supermoon.
A full moon that occurs at perigee appears 14% bigger and 30% brighter than a full moon that occurs at apogee, the farthest point from the earth in its orbit.
No lunar eclipse at every full moon
A lunar eclipse occurs only at the full moon phase, but not at every full moon.
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth is in a straight line between the Sun and the Moon and the Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon.
However, it doesn’t happen at every full moon phase because the lunar orbit is tilted about 5° with respect to the ecliptic, the plane of the earth’s orbit around the sun.
When the plane of the lunar orbit around the earth intersects with the plane of the earth’s orbit around the sun at full moon phase then a lunar eclipse occurs.
Read about all eight phases of the moon: New moon Waxing crescent First quarter Waxing gibbous Full moon Waning gibbous Third quarter Waning crescent
Please follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.