A first quarter moon is a waxing half-full moon
A waxing moon starts right after a new moon and lasts until it becomes a full moon. During a waxing moon, the illuminated area of the moon increases from 0% (new moon) to 100% (full moon). Here waxing means increasing or growing.
Now a first quarter moon appears in the middle way between a new moon and a full moon when the moon is exactly 50% illuminated. As a first quarter moon is 50% illuminated that’s why it looks like a half-full moon. Please remember, it is the opposite half compared to a third quarter moon.
The age of a first quarter moon is about 7 days

A lunar cycle starts from the new moon phase and a first quarter moon is seen in the sky about one week after the new moon. So the age of a first quarter moon is about 7 days.
Meaning of the first quarter moon
A first quarter moon is when the moon travels exactly one quarter area or 1/4 area or 90° area out of 360 degrees in its orbit around the Earth.
We measure a first quarter area or 90° area from the position of a new moon (when the Moon is located in front of the Sun with respect to the Earth).
Rise and set time of a first quarter moon
A first quarter moon rises around noon (at around 12 p.m. local time) in the east, reaches highest point (overhead point) in the sky around the time of sunset and sets around midnight (at around 12 a.m. local time) in the west.
So a first quarter moon is best visible around the time of sunset when it’s high in the sky.
Duration of a first quarter moon
A first quarter moon occurs at a precise moment when the moon travels exactly one quarter area in its orbit around the earth. As a first quarter moon occurs at a precise moment in time that’s why it has no duration.
However a first quarter moon looks like a half-full moon around 3 days in our naked eye. It’s the day of first quarter moon, before the day of first quarter moon and after the day of first quarter moon.
First quarter moon looks opposite in opposite hemispheres
A half-full moon is seen in the sky from anywhere in the world during a first quarter moon however it looks opposite in opposite hemispheres.
Right half of the moon is seen from the Northern Hemisphere and left half of the moon is seen from the Southern Hemisphere during a first quarter moon.
People living in the southern hemisphere (south of the equator) observe the same first quarter moon from opposite angles than the people living in the northern hemisphere (north of the equator) and the moon looks upside down.
A first quarter moon is only 8% bright of a full moon
Though we see a 50% lighted part of the moon or a 50% illuminated moon during a first quarter moon but it’s only 8% bright of a full moon.
Don’t you believe me? Let’s calculate it.
As we know, the apparent magnitude of a full moon is -12.7, and the apparent magnitude of a first quarter moon is -10.
Please remember, the lower the value, the higher the magnitude of an astronomical object.
Now the relation between apparent magnitude and the brightness of an object is not linear, but it’s exponential and follows the below equation.
2.512^(M – m) = change in brightness
So a difference of one magnitude corresponds to a 2.512 times change in brightness.
Here change in magnitude is -12.7 – (-10) = -2.7 so change in brightness = 2.512^(-2.7) = 0.08. That’s why a first quarter moon is only 8% bright of a full moon and the brightness is reduced by 12 times.
So a 50% illuminated moon (first quarter) is only 8% bright of a full moon and believe it or not, a 95% illuminated moon is 50% bright of a full moon.
The first quarter of the moon is an ideal time to observe the moon’s craters and mountains
The first quarter of the moon is an ideal time to observe the moon’s craters and mountains along the terminator of the moon if you have a pair of binoculars or a telescope.
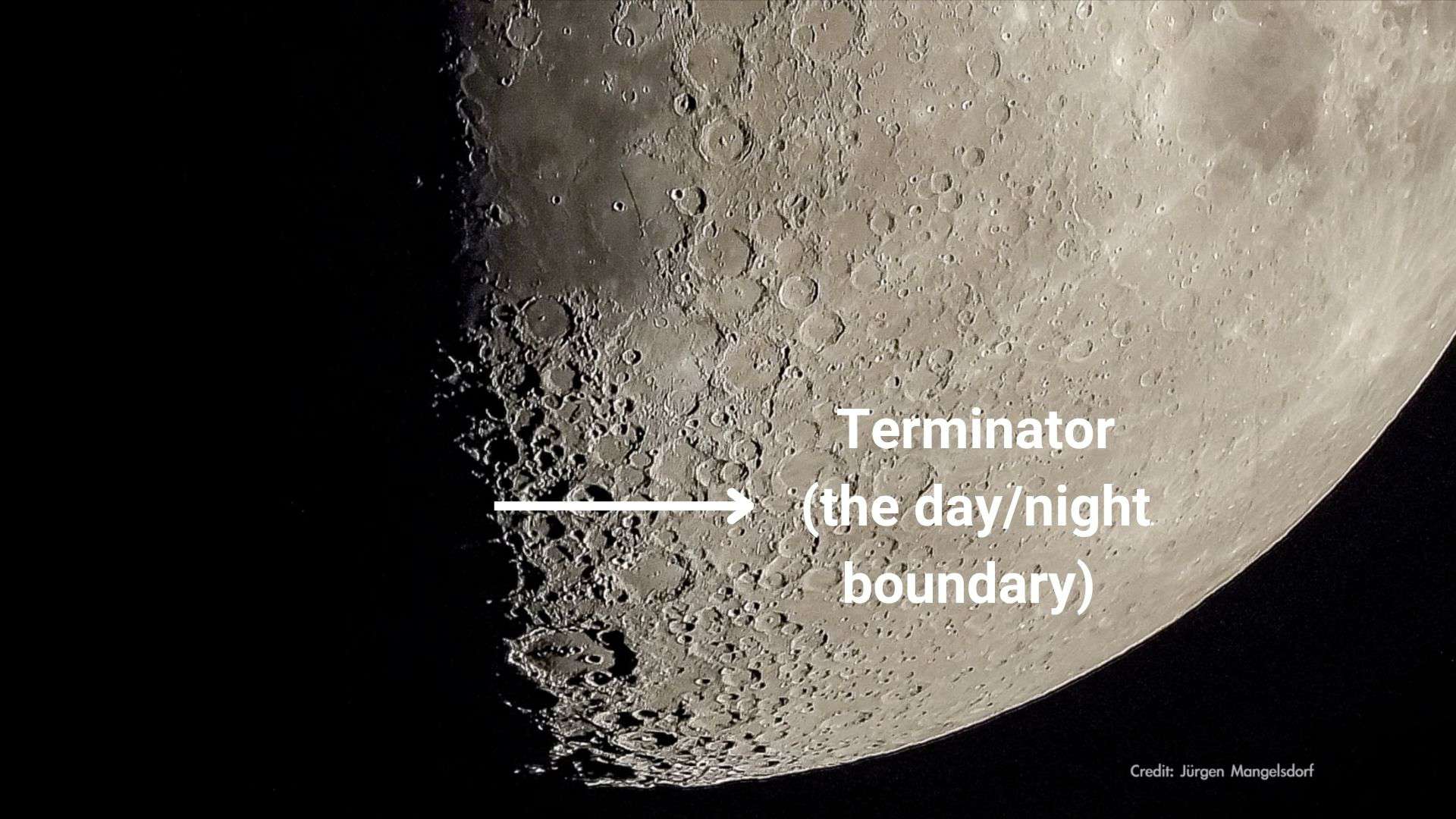
The terminator is an imaginary line that divides the lighted part (day) and the unlighted part (night) of the moon. In short, it’s the boundary between day and night on the moon, so it signifies the twilight zone on the lunar surface.
During a first quarter moon, the terminator line divides the moon into two equal halves. So we see 50% lighted parts of the moon and 50% unlighted parts of the moon.
As a first quarter moon is neither completely illuminated like a full moon nor completely dark like a new moon, that’s why it’s the best time to observe the moon’s craters and mountains.
A first quarter moon occurs once every 29.531 days
A first quarter moon occurs once every 29.531 days when the moon rises around noon, reaches its highest point in the sky around the time of sunset, and sets around midnight.
Read about all eight phases of the moon: New moon Waxing crescent First quarter Waxing gibbous Full moon Waning gibbous Third quarter Waning crescent
Please follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.



