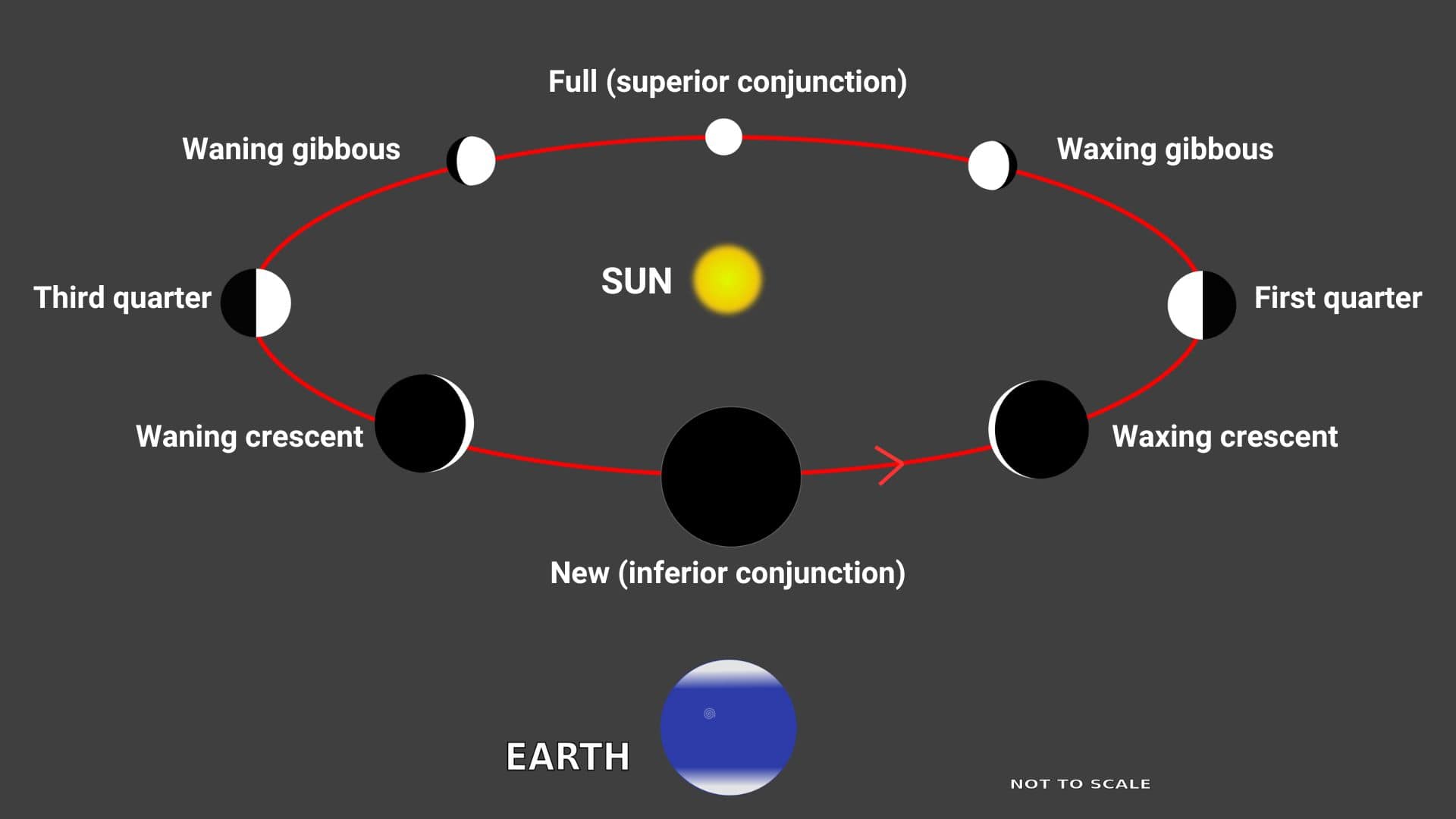
Mercury at superior conjunction marks the disappearance of Mercury from the eastern sky as a morning object and its transition to the western sky as an evening object.
Mercury at superior conjunction
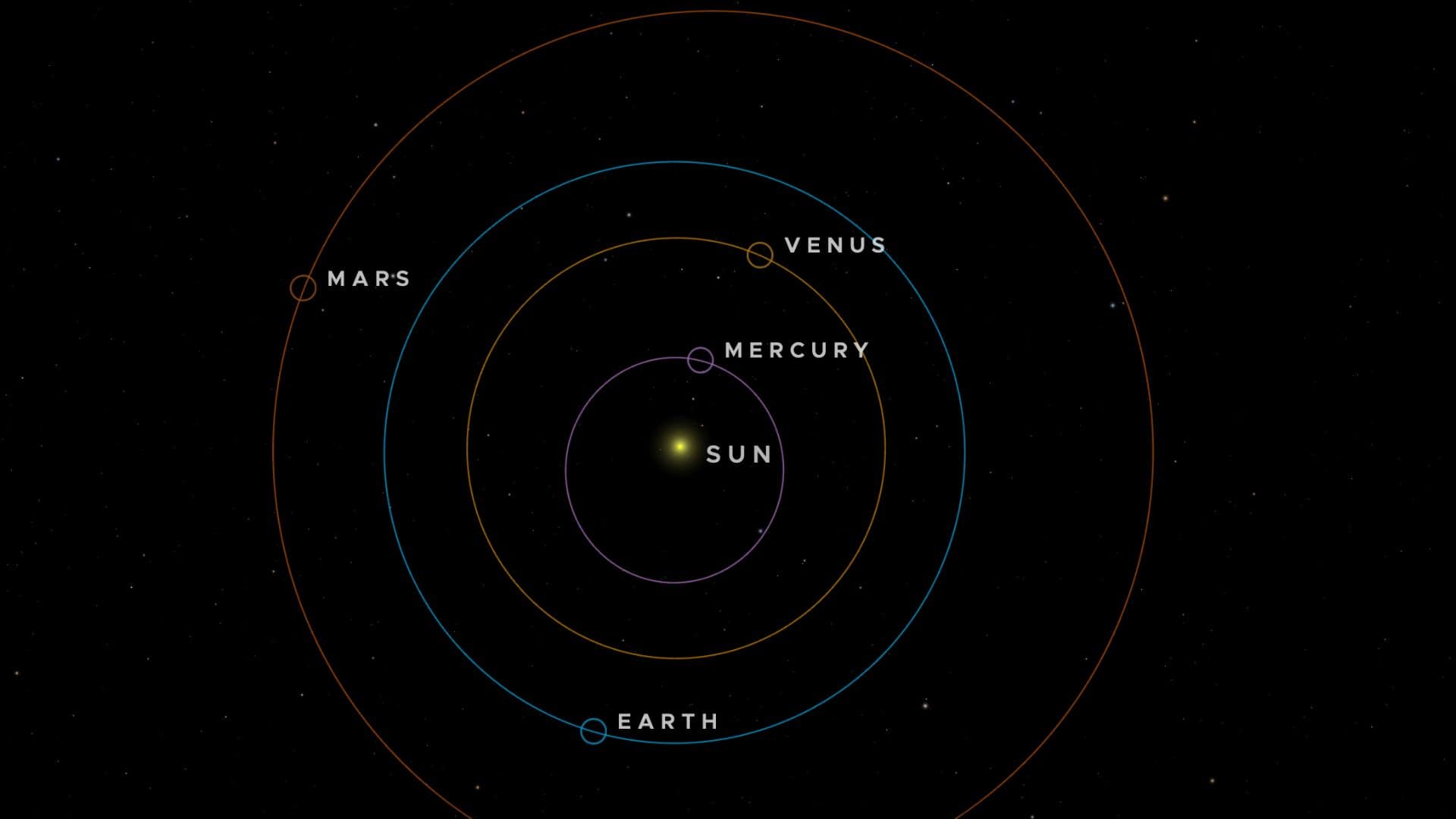
Mercury at superior conjunction position in its orbit, meaning it is located on the opposite side of the sun with respect to the earth.
If the sun is located exactly between the earth and Mercury in a straight line, then Mercury disappears behind the sun, and we call it the occultation of Mercury. So occultation is a special case of superior conjunction.
During the superior conjunction position, planet Mercury appears to pass closest to the sun (about a degree) on our sky’s dome as it is located behind the sun.
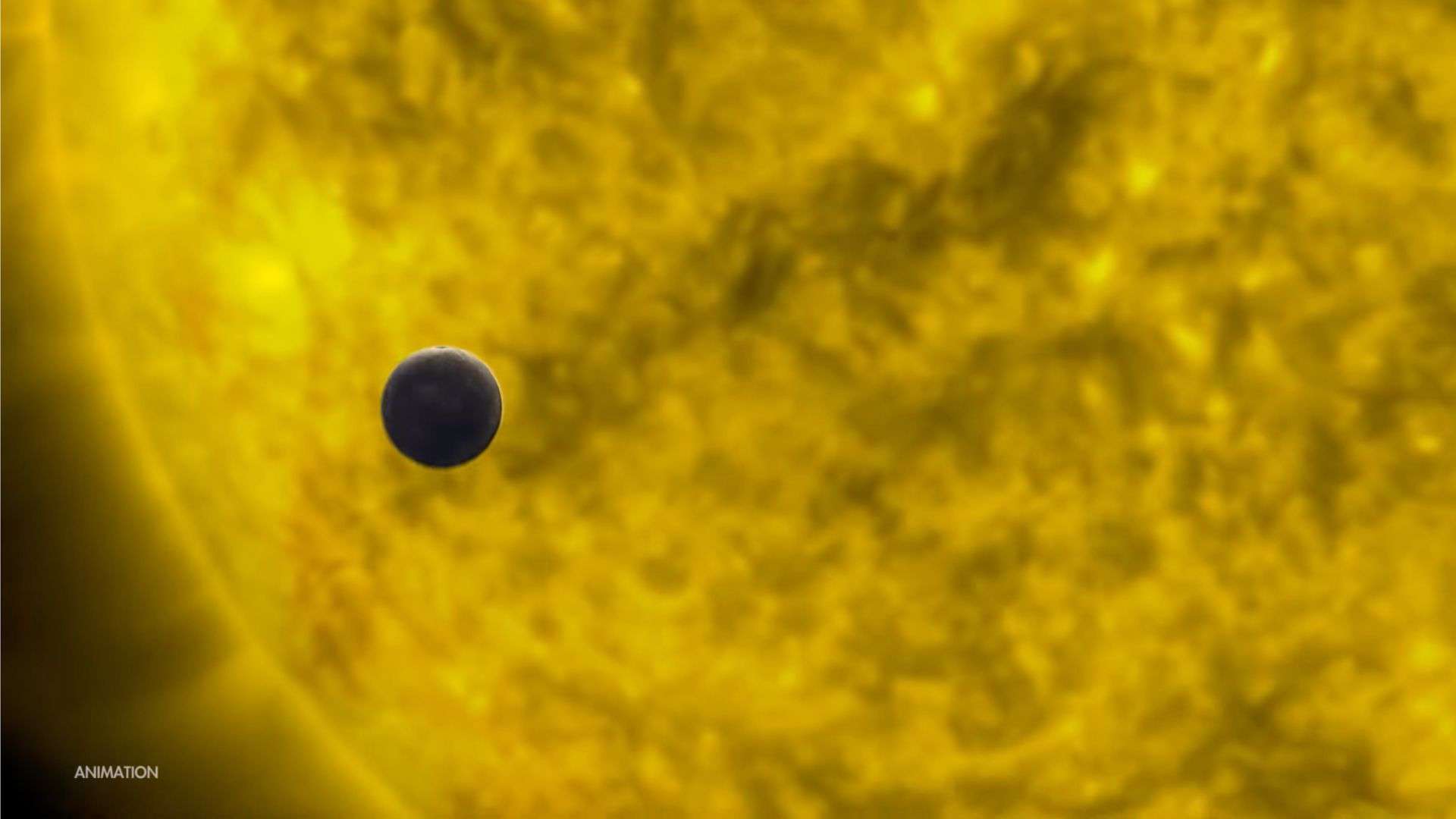

It’s normally not possible to observe planet Mercury during the superior conjunction as it lost in the Sun’s glare. You have to wait for few days to observe Mercury again and after superior conjunction it will be visible in the western sky following sunset.
Mercury is the fastest moving planet in our solar system, so it usually takes a little over a month to reach maximum angular separation (called greatest eastern elongation) on our sky’s dome from the superior conjunction position.
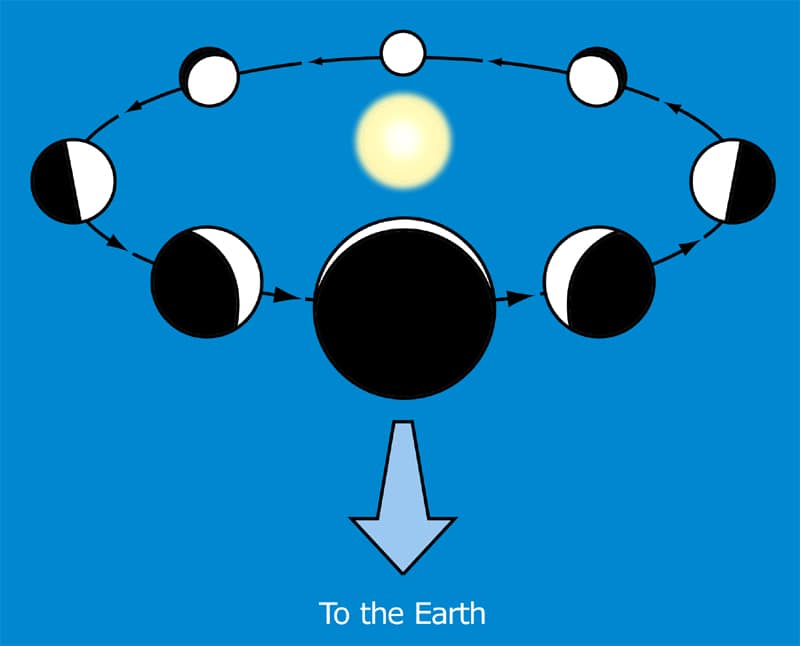
During the superior conjunction, planet Mercury appears fully illuminated (100% illuminated), or its “full” phase and smallest, as it’s located on the other side of the sun.
Mercury Farthest from the Earth
During the superior conjunction, planet Mercury reaches its apogee i.e. farthest distance from the Earth.
Mercury at superior conjunction in 2024
Planet Mercury will reach its next superior conjunction on June 14, 2024, at 16:00 UTC (12 p.m. EDT).
| Date | Time (UTC) |
|---|---|
| February 28, 2024 | 08:00 |
| June 14, 2024 | 16:00 |
| September 30, 2024 | 21:00 |
| February 09, 2025 | 12:00 |
How often does Mercury reach superior conjunction?
Mercury reaches a superior solar conjunction once every 116 days. It’s called the synodic period of Mercury. It is the interval of time Mercury takes to orbit the sun and come back to the same position with respect to the Earth. It is slightly greater than the actual orbital period of Mercury (88 days) because our Earth is also in motion in its orbit.
Mercury events in 2024
| Date | Events | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| January 12, 2024 | Mercury at greatest western elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the eastern sky before sunrise |
| February 28, 2024 | Mercury at superior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from a morning object to an evening object |
| March 24, 2024 | Mercury at greatest eastern elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the western sky following sunset |
| April 11, 2024 | Mercury at inferior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from an evening object to a morning object |
| May 9, 2024 | Mercury at greatest western elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the eastern sky before sunrise |
| June 14, 2024 | Mercury at superior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from a morning object to an evening object |
| July 22, 2024 | Mercury at greatest eastern elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the western sky following sunset |
| August 19, 2024 | Mercury at inferior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from an evening object to a morning object |
| September 5, 2024 | Mercury at greatest western elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the eastern sky before sunrise |
| September 30, 2024 | Mercury at superior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from a morning object to an evening object |
| November 16, 2024 | Mercury at greatest eastern elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the western sky following sunset |
| December 06, 2024 | Mercury at inferior conjunction | Transition of Mercury from an evening object to a morning object |
| December 25, 2024 | Mercury at greatest western elongation | Best time to watch Mercury in the eastern sky before sunrise |
Read about all Mercury events: Mercury at inferior conjunction Mercury at greatest western elongation Mercury at superior conjunction Mercury at greatest eastern elongation
Please follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.