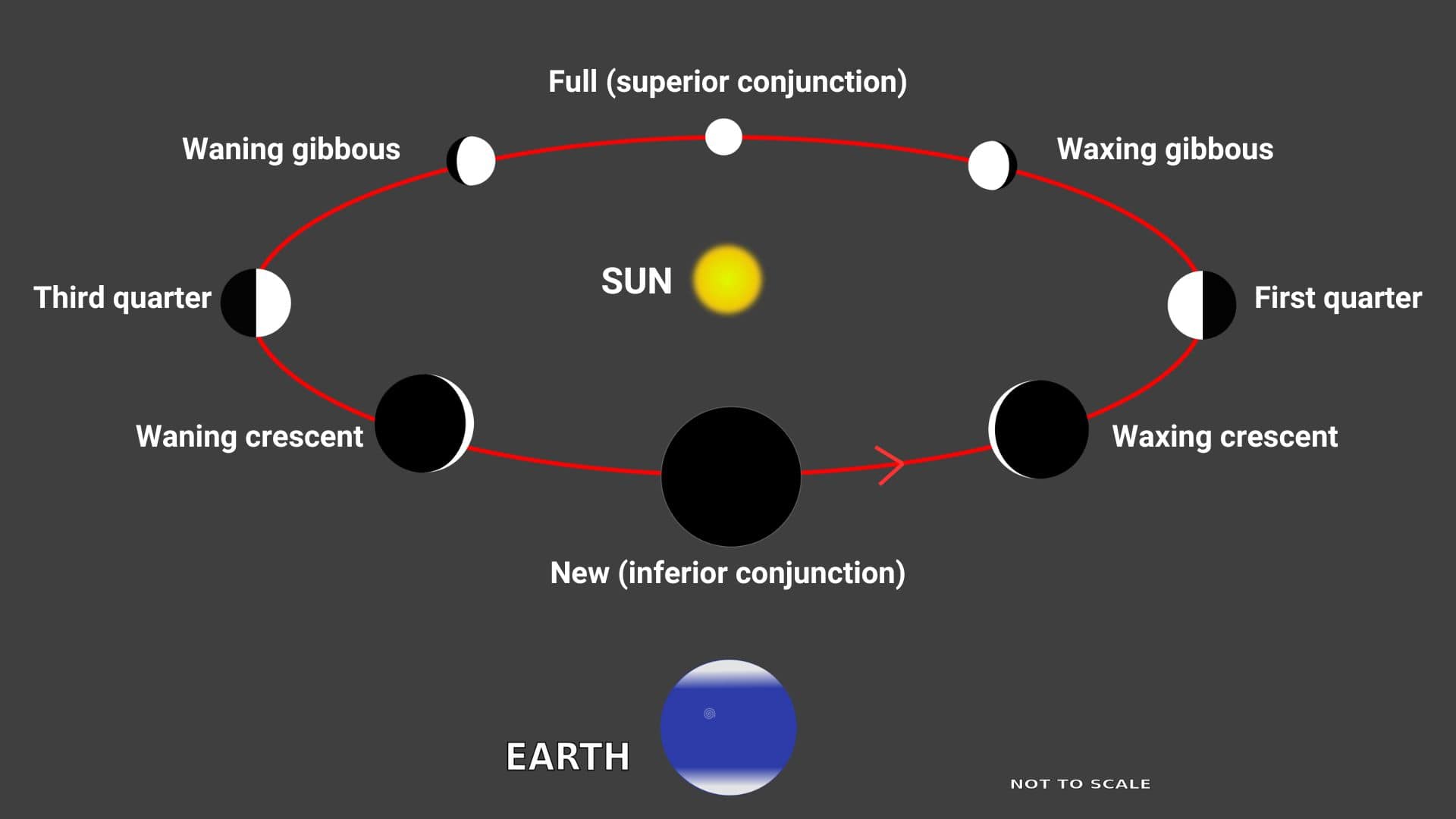
Universal Time (UT1)
When we measure time based on the Earth’s rotation relative to the Sun, it is called solar time. As solar time is used universally, that’s why it’s called Universal Time (UT1). The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) always monitors the Earth’s rotation and Universal Time (UT1).
Now the rotation of the earth is gradually slowing due to the tidal force of the moon and the mean solar day is gradually increasing. Due to this trouble, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) comes into place.
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
When we measure time based on the oscillations of atoms (International Atomic Time), it is called Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and it is always adjusted to remain within 0.9 seconds of Universal Time (UT1) by occasionally adding a “leap second.”
UTC is the standard reference for time zones around the world and is used by GPS.
Time zones
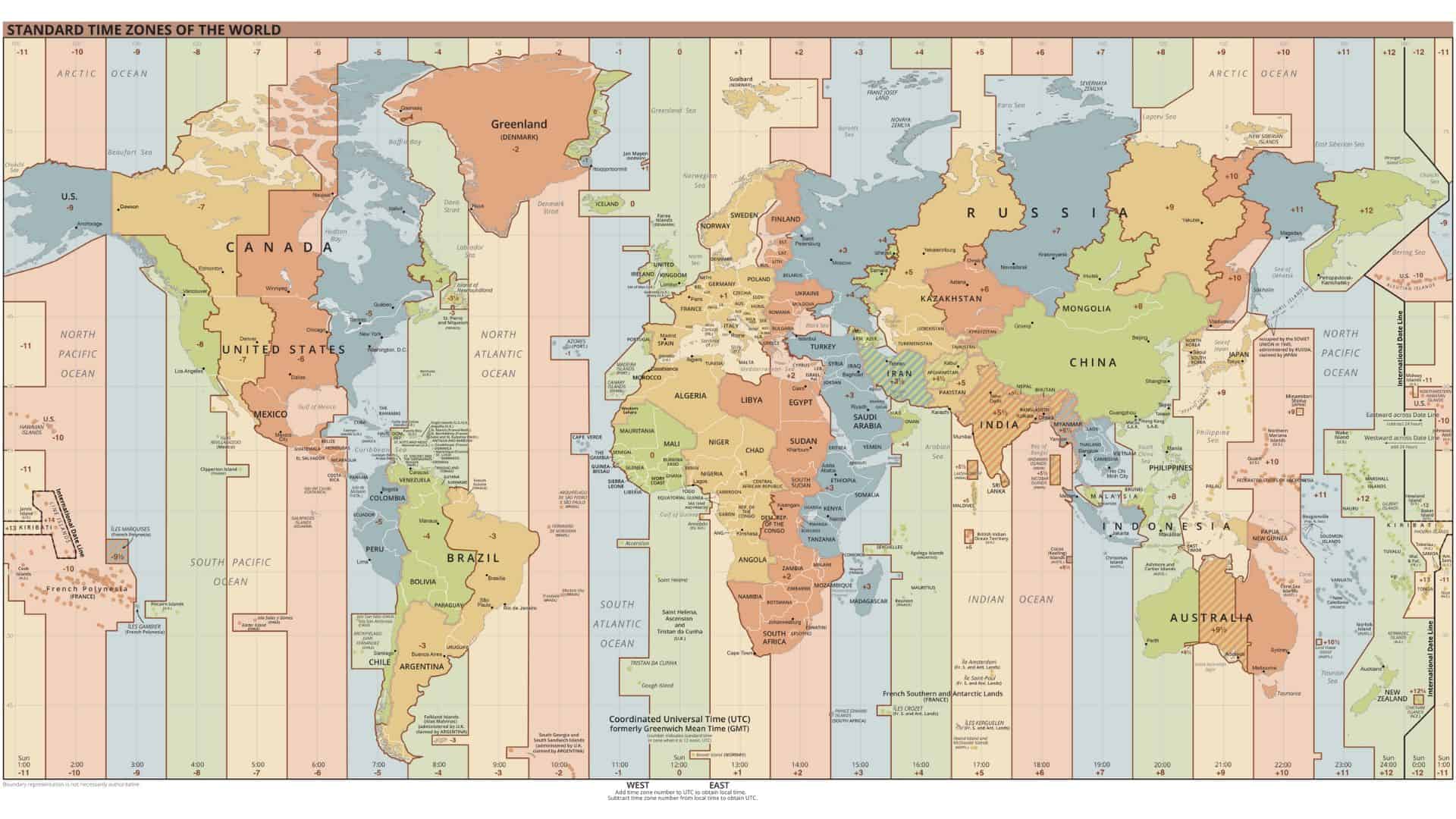
A time zone is an area that exhibits the same local time for legal, commercial, and social purposes.
Many time zones have been created on the world map by simply adding or subtracting hours from UTC. For instance, the time zone, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), is set equal to UTC, and other time zones range from UTC – 12 hours to UTC + 14 hours.
Time zones that are located east of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) are ahead of UTC, and time zones that are located west of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) are backward of UTC.
Please remember UTC is a reference time which is always synchronized with Universal Time and GMT is a time zone which is equals to UTC time.
Convert UTC time to your local time
The Americas
Hawaii Standard Time (HST ) = UTC – 10 hours
Alaska Standard Time (AKST) = UTC – 9 hours
Alaska Daylight Time (AKDT) = UTC – 8 hours
Pacific Standard Time (PST) = UTC – 8 hours
Pacific Daylight Time (PDT) = UTC – 7 hours
Mountain Standard Time (MST) = UTC – 7 hours
Mountain Daylight Time (MDT) = UTC – 6 hours
Central Standard Time (CST) = UTC – 6 hours
Central Daylight Time (CDT) = UTC – 5 hours
Eastern Standard Time (EST) = UTC – 5 hours
Eastern Daylight Time (EDT) = UTC – 4 hours
Atlantic Standard Time (AST) = UTC – 4 hours
Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT) = UTC – 3 hours
Newfoundland Standard Time (NST) = UTC – 3.5 hours
Newfoundland Daylight Time (NDT) = UTC – 2.5 hours
Please note that most American countries observe Daylight Saving Time, which starts at 2 a.m. on the second Sunday of March and ends at 2 a.m. on the first Sunday of November every year. You have to add one hour to the standard time to get Daylight Saving Time.
Europe, Africa and the Middle East
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) = UTC + 0 hour
British Summer Time (BST) = UTC + 1 hours
Central European Time (CET) = UTC + 1 hours
Central European Summer Time (CEST) = UTC + 2 hours
Eastern European Time (EET) = UTC + 2 hours
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) = UTC + 3 hours
Moscow Standard Time (MSK) = UTC + 3 hours
Turkey Time (TRT) = UTC + 3 hours
Saudi Arabia Standard Time (SAST) = UTC + 3 hours
Gulf Standard Time (GST) = UTC + 4 hours
Most European countries also observe Daylight Saving Time. In Europe, Daylight Saving Time is referred to as Summer Time, which starts at 1 a.m. GMT on the last Sunday of March and ends at 1 a.m. GMT on the last Sunday of October every year. You have to add one hour to the standard time to get Summer Time.
Asia and Oceania
Afghanistan Time (AFT) = UTC + 4.5 hours
Pakistan Standard Time (PKT) = UTC + 5 hours
Indian Standard Time (IST) = UTC + 5.5 hours
Bangladesh Standard Time (BST) = UTC + 6 hours
Indochina Time (ICT) = UTC + 7 hours
China Standard Time (CST) = UTC + 8 hours
Australian Western Standard Time (AWST) = UTC + 8 hours
Japan Standard Time (JST) = UTC + 9 hours
Australian Central Time (ACT) = UTC + 9.5 hours
Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST) = UTC + 10 hours
New Caledonia Time (NCT) = UTC + 11 hours
New Zealand Standard Time (NZST) = UTC + 12 hours
Please follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.