China’s Chang’e 6 spacecraft has successfully entered lunar orbit on May 8, 2024, at 10:12 a.m. local time (02:12 UTC), according to the Chinese space agency CNSA.
Chang’e 6 aims to be the first spacecraft to land on the far side of the moon, collect samples and bring them back to the earth.
It is harder to land on the lunar far side (the side of the moon that can’t be seen from the earth) than on the near side (the side of the moon that is seen from the earth).
It is not possible to communicate from the earth directly when the spacecraft is on the lunar far side. Chang’e 6 spacecraft depends on the Queqiao-2 (Magpie Bridge 2) relay satellite to communicate to and from the earth.
To date, it is the most difficult lunar mission China has ever launched.
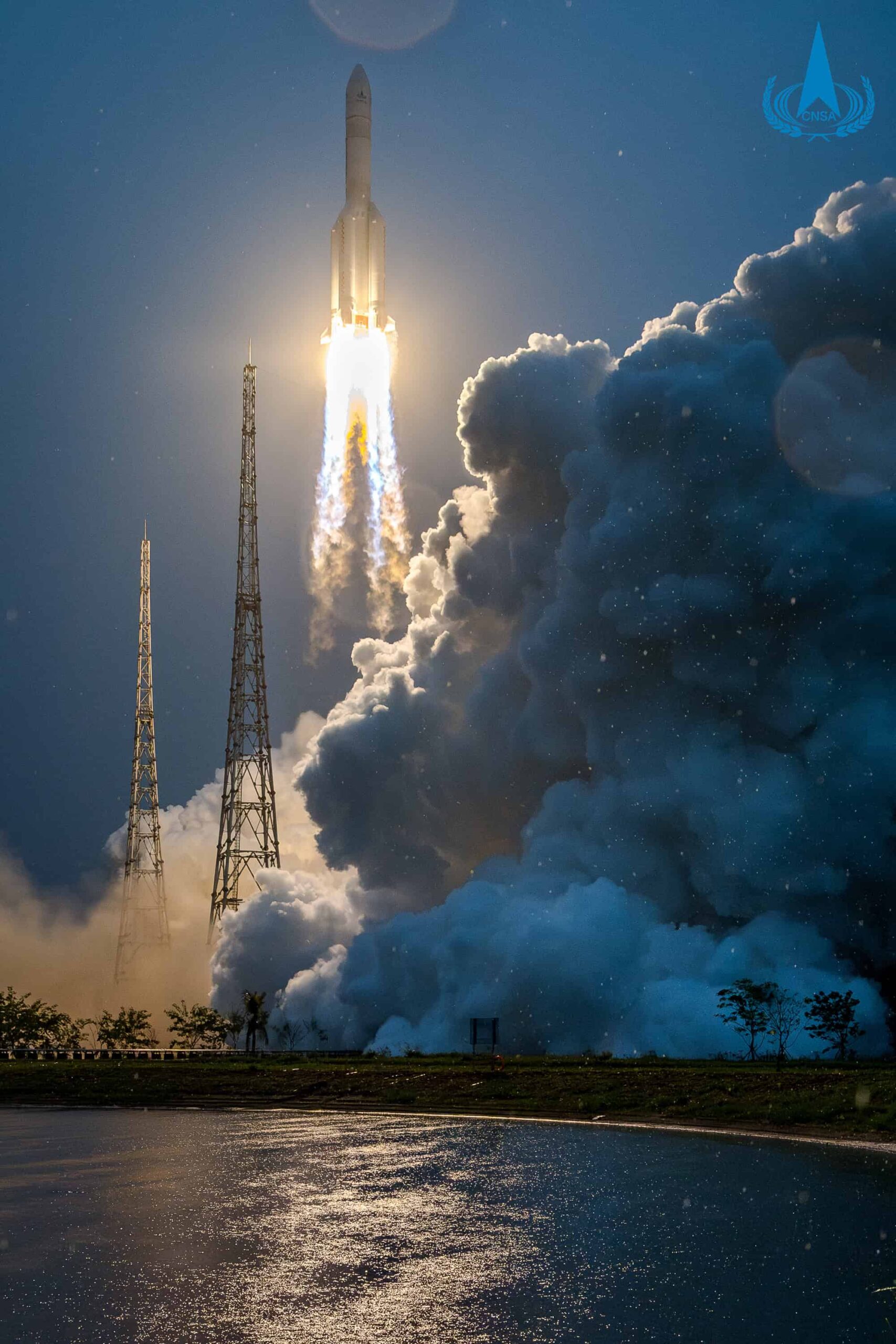
Chang’e 6 spacecraft was launched on a Long March 5 heavy-lift carrier rocket on May 3, 2024, at about 5:27 p.m. local time (09:27 UTC) from the Wenchang Space Launch Center, China.
About 37 minutes after the launch, the rocket had placed the Chang’e 6 spacecraft into an earth-moon transfer orbit and completed its job.

Since then, the spacecraft has been traveling alone, and on May 8, the spacecraft entered a lunar orbit. To do that, the mission control team conducted a key braking maneuver that lowered the spacecraft’s velocity compared to the lunar escape speed. As a result, the moon’s gravity captured the spacecraft and made it move into a lunar orbit.
After the lunar orbit insertion, the spacecraft’s altitude and inclination in the lunar orbit have been adjusted with the help of the Queqiao-2 relay satellite.
If everything goes according to plan, then the spacecraft will land within the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin, a vast lunar depression on the far side of the moon. However, the Chinese space agency, the China National Space Administration (CNSA), has yet to announce its landing date.
The duration of the Chang’e 6 mission is about 53 days, from the launch to sample collection and then return to the earth.
Related article: China launches Chang’e 6 mission to collect lunar far side samples
Please bookmark Spaceandtelescope.com or follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.