China’s Chang’e 6 spacecraft brought back precious lunar rocks and soil from the far side of the moon to Earth for the first time ever.
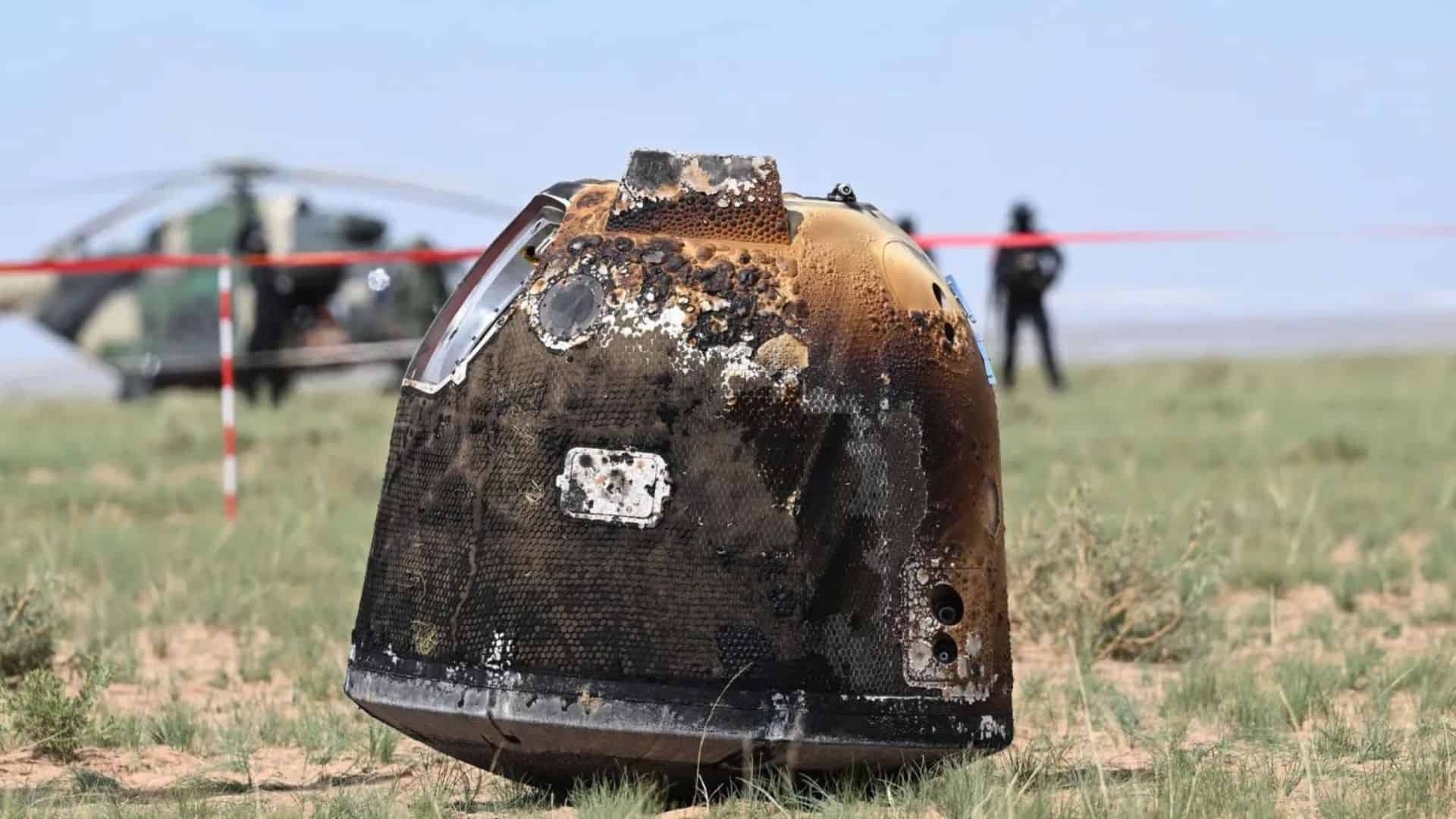
The spacecraft landed with lunar samples in the Inner Mongolia desert on Tuesday, June 25, 2024, after completing its 53-day mission.
After landing, the space probe was collected and taken to Beijing for sample recovery.
The mission is historic because no other country has achieved this feat so far, i.e., to land on the far side of the moon and, from there, collect lunar materials and bring them back to Earth.
Landing on the far side of the moon (the side of the moon that cannot be seen from Earth) is tough as it is filled with craters and direct communication is not possible.
Chang’e 6 spacecraft was launched on a Long March 5 rocket on May 3, 2024. It entered lunar orbit on May 8, 2024.
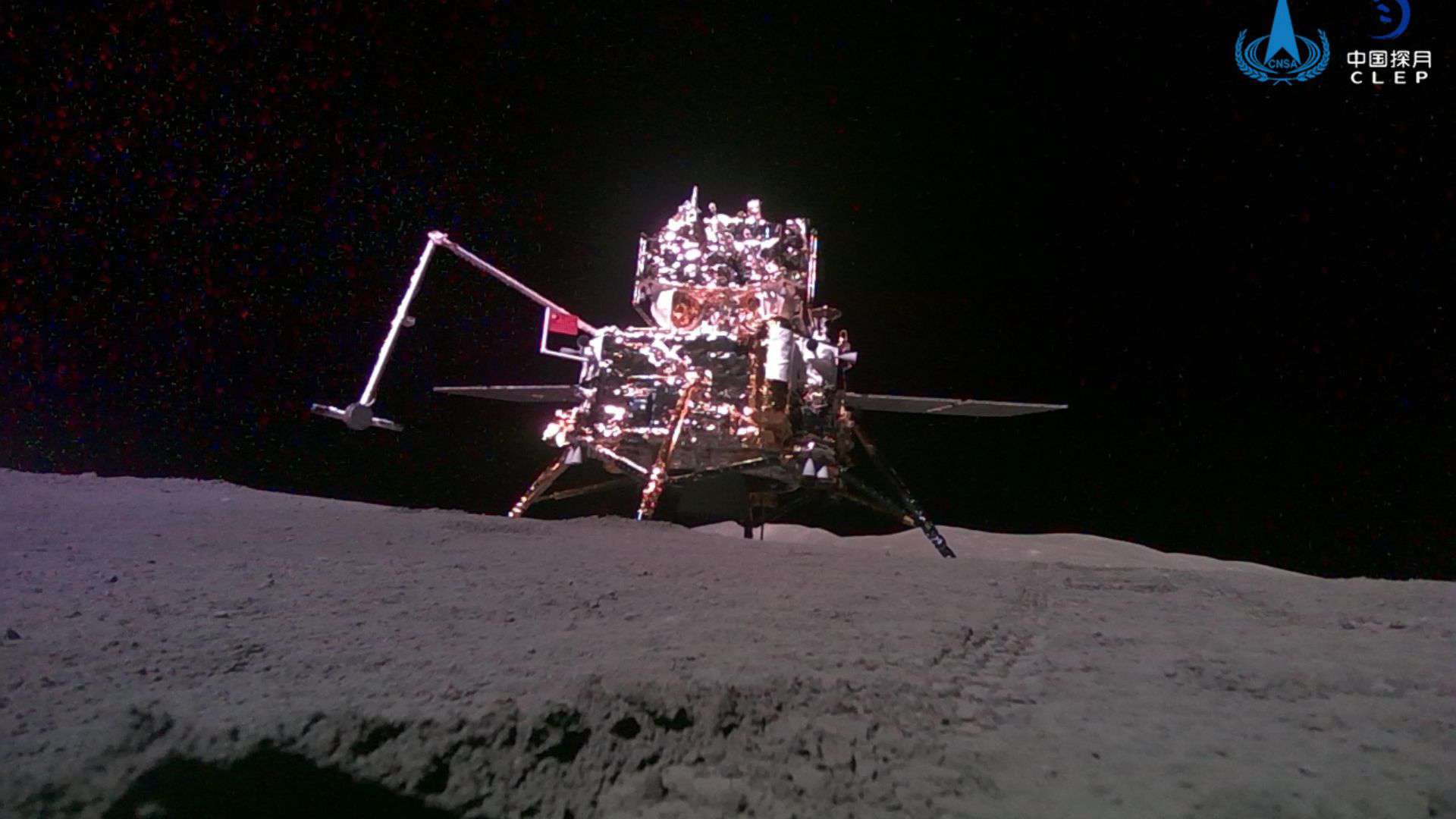

The spacecraft landed at the southern part of the 490-km-diameter Apollo crater in the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin on the far side of the moon on June 1, 2024.
The spacecraft used a drilling tool and a mechanical arm to collect up to 2 kilograms of lunar samples.
After the successful lunar sample collection, the ascender module (ascender rocket) of the spacecraft brought the lunar samples to the lunar orbit and docked with the combination of the orbiter and the re-entry module on June 6, 2024.
Finally, the re-entry module of Chang’e 6, which is capable of withstanding atmospheric heat, landed on Earth on June 25, 2024, at 06:07 UTC.
Throughout the mission on the far side of the moon, the spacecraft communicated with the earth control room through the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, as direct communication was not possible.
There is no doubt that China has achieved remarkable success in its lunar exploration program in a very short period of time. China aims to send its first astronaut to the lunar surface by 2030. China’s moon missions so far are summarized below.
| Mission Name | Launch Date | Mission Type | Objectives | Mission Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chang’e 1 | October 24, 2007 | Orbiter | Obtain three-dimensional images of the lunar surface and map the abundance of chemical elements on the lunar surface | Successful |
| Chang’e 2 | October 1, 2010 | Orbiter | Obtain high-resolution images of the lunar surface to help in selecting future landing sites and a key test for soft landing on the moon | Successful |
| Chang’e 3 | December 1, 2013 | Lander and Rover | Achieve first soft landing on the lunar surface and exploration with the Yutu rover | Successful |
| Chang’e 4 | December 7, 2018 | Lander and Rover | Achieve first soft landing on the far side of the moon and exploration with the Yutu-2 rover | Successful |
| Chang’e 5 | November 23, 2020 | Sample-return mission | Collect lunar samples and bring them back to Earth | Successful |
| Chang’e 6 | May 3, 2024 | Far side sample-return mission | Collect lunar samples from the far side of the moon and bring them back to Earth | Successful |
Please bookmark Spaceandtelescope.com or follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.