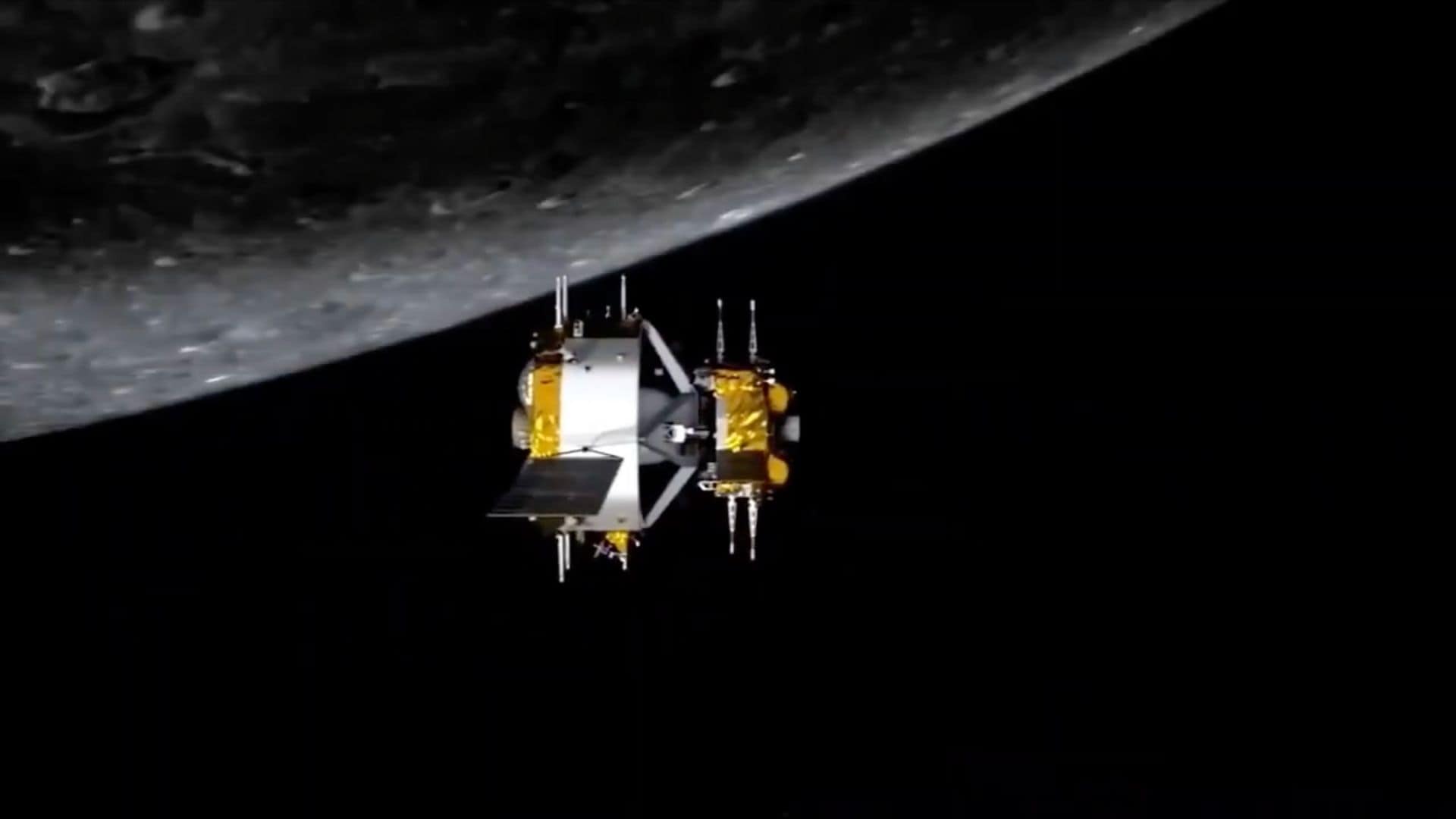
China’s Chang’e 6 sample-return spacecraft is one step closer to returning far side lunar samples, as the ascender module of the spacecraft brought the lunar samples to the lunar orbit and docked with the combination of the orbiter and the re-entry module.
Chang’e 6 spacecraft landed within the Apollo crater of the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) basin on the far side of the moon at 22:23 UTC on June 1, 2024.
The spacecraft collected lunar samples from June 2 to 3, as planned. After the successful sample collection, an ascent vehicle (ascender rocket) was launched from the lunar surface at 23:38 UTC on June 3.
This ascent vehicle of the spacecraft met with the combination of the orbiter and the re-entry module at 06:48 UTC on June 6, 2024, in the lunar orbit and safely transferred the lunar sample container to the re-entry module at 07:24 UTC on June 6, 2024, according to the Chinese space agency CNSA.
If everything goes according to plan, then the re-entry module will bring the samples back to earth from lunar orbit around June 25 and will land at the Siziwangqi space landing site in Inner Mongolia.
It is the second time that a Chinese spacecraft has achieved successful docking in the lunar orbit after the agency’s Chang’e 5 spacecraft. Chang’e 5 brought back lunar samples from the near side of the moon in 2020.
After successful completion of the mission, Chang’e 6 will become the first sample-return spacecraft from the far side of the moon. No other country has achieved this feat so far.
There is no doubt that China has achieved remarkable success in its lunar exploration program in a very short period of time. China aims to send its first astronaut to the lunar surface by 2030. China’s moon missions so far are summarized below.
| Mission Name | Launch Date | Mission Type | Objectives | Mission Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chang’e 1 | October 24, 2007 | Orbiter | Obtain three-dimensional images of the lunar surface and map the abundance of chemical elements on the lunar surface | Successful |
| Chang’e 2 | October 1, 2010 | Orbiter | Obtain high-resolution images of the lunar surface to help in selecting future landing sites and a key test for soft landing on the moon | Successful |
| Chang’e 3 | December 1, 2013 | Lander and Rover | Achieve first soft landing on the lunar surface and exploration with the Yutu rover | Successful |
| Chang’e 4 | December 7, 2018 | Lander and Rover | Achieve first soft landing on the far side of the moon and exploration with the Yutu-2 rover | Successful |
| Chang’e 5 | November 23, 2020 | Sample-return mission | Collect lunar samples and bring them back to Earth | Successful |
| Chang’e 6 | May 3, 2024 | Far side sample-return mission | Collect lunar samples from the far side of the moon and bring them back to Earth | Ongoing |
Please bookmark Spaceandtelescope.com or follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.