NASA’s historic Ingenuity Mars helicopter has reached the end of its mission due to the damage of its rotor blade during its 72nd flight above the Red Planet on Thursday, January 18, 2024.
“The historic journey of Ingenuity, the first aircraft on another planet, has come to end,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson on Thursday, January 25, 2024.
“That remarkable helicopter flew higher and farther than we ever imagined and helped NASA do what we do best – make the impossible, possible. Through missions like Ingenuity, NASA is paving the way for future flight in our solar system and smarter, safer human exploration to Mars and beyond.”
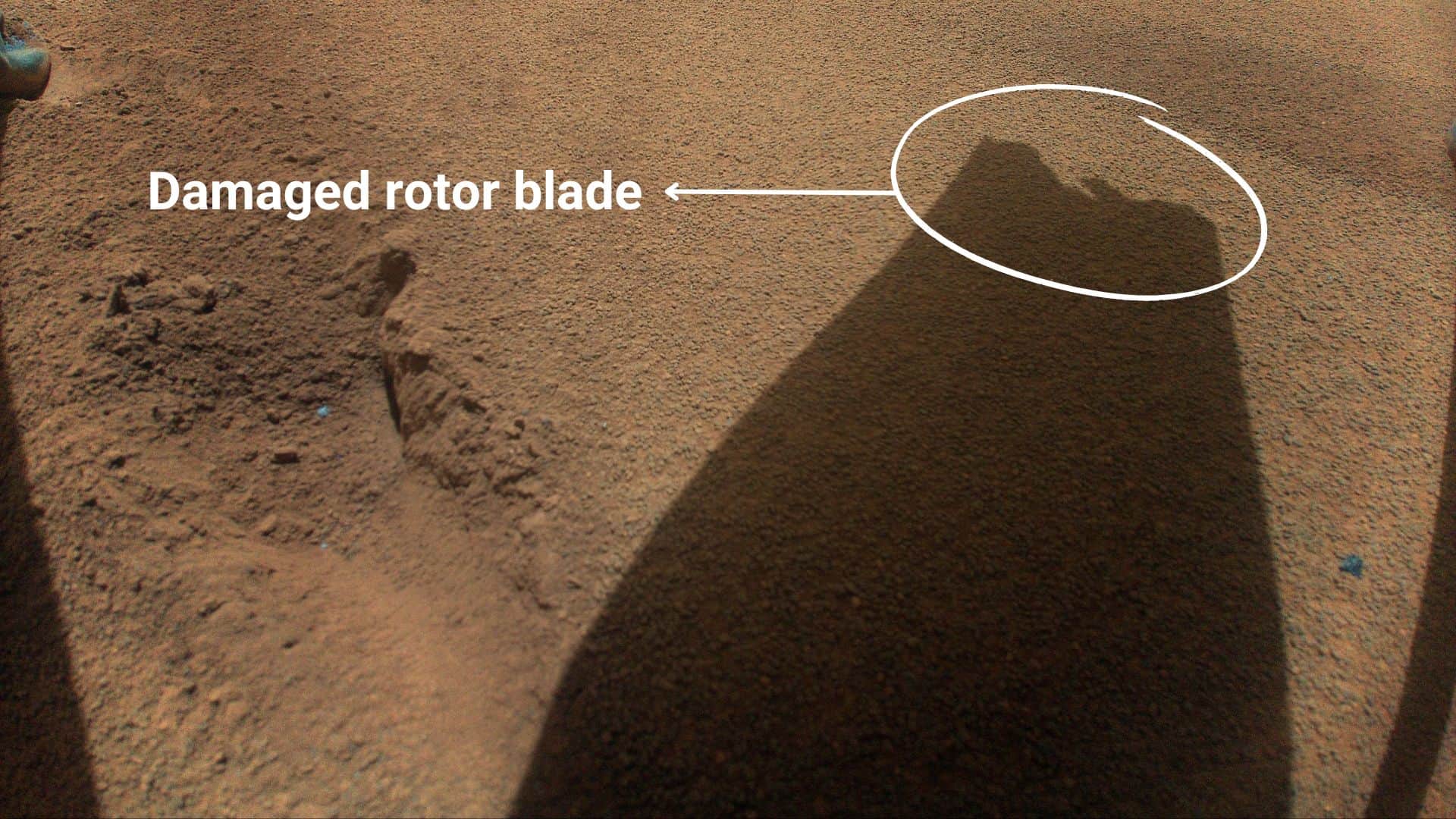
On the 72nd flight, the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter successfully climbed to its assigned maximum altitude of 40 feet (12 meters) and hovered for 4.5 seconds before starting its descent at a velocity of 3.3 feet per second (1 meter per second). However it didn’t cover any horizontal distance as it was a quick pop-up vertical flight.
During its planned descent, communications between the Ingenuity helicopter and Perseverance rover terminated early, prior to touchdown.
The cause of the communications dropout is still unknown, and it will be investigated, said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
NASA’s JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory) team, which manages the rover and helicopter, has found that at least one of the helicopter’s rotor blades has been damaged during the emergency landing on its 72nd flight, and it’s no longer capable of flight.
During the final 72nd flight, the Ingenuity Mars helicopter was on the Chi airfield of Jezero Crater of Mars.
The goal of the 72nd flight was to check out the helicopter’s systems, as the helicopter landed earlier than expected on its 71st flight.
The Ingenuity helicopter is a small (weighing only 1.8 kilograms) autonomous aircraft. It made history by achieving the first powered, controlled flight on another planet on April 19, 2021.
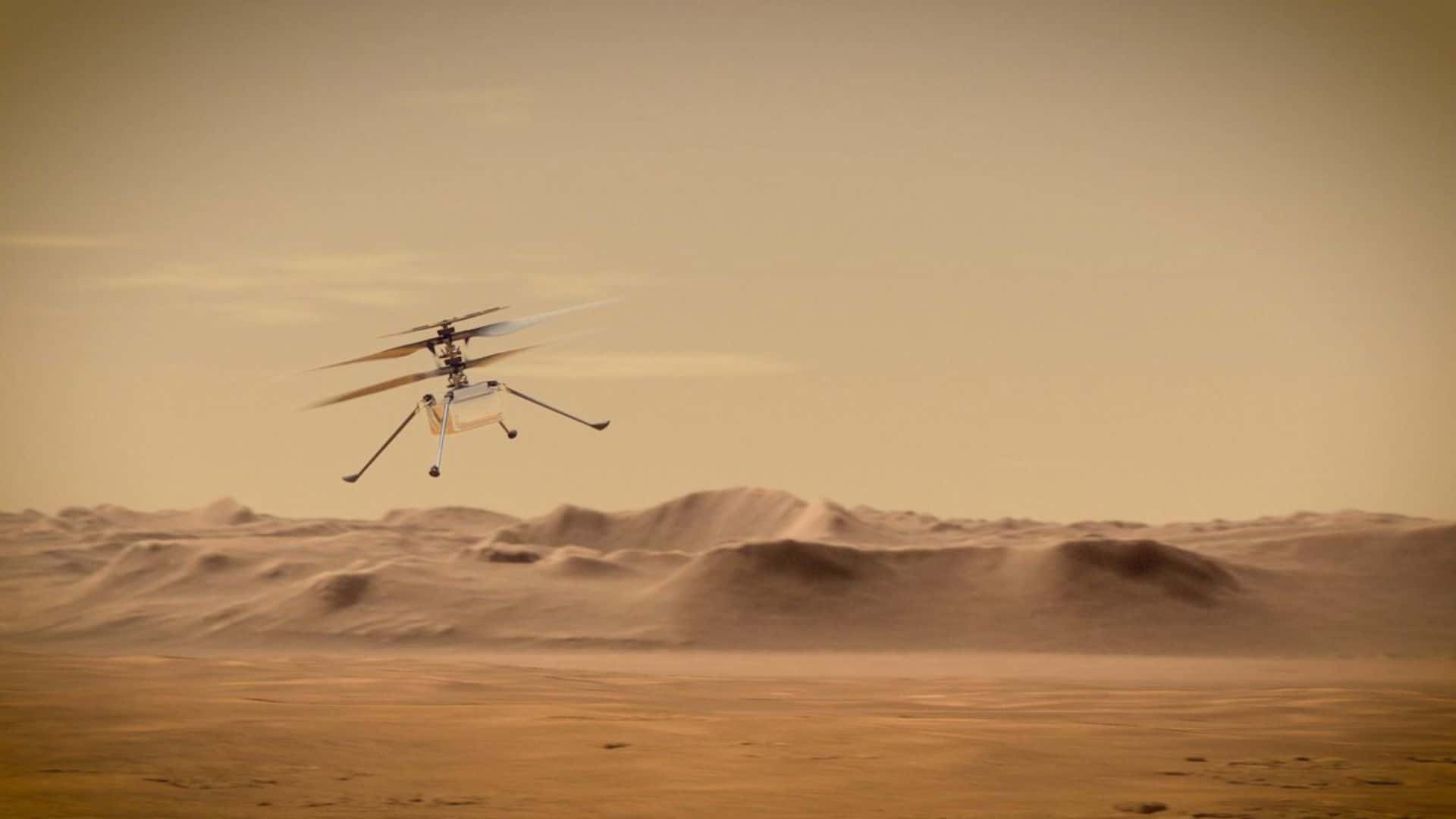

NASA’s Perseverance rover carried the Ingenuity helicopter to the surface of Mars on February 18, 2021, attached with its belly.
The Ingenuity Mars helicopter has flown a total of 72 flights since its first flight above the Mars planet on April 19, 2021.
Over the course of its 72 Mars flights, Ingenuity helicopter has flown a distance of 17 kilometers (11 miles) in 128.8 minutes according to the mission’s flight log.
NASA has spent about 85 million dollars to build the Ingenuity Mars helicopter, accommodate it on Perseverance, and operate the helicopter on Mars.
The helicopter has ended its extended mission on January 18, 2024. However it was built to attempt up to five test flights within a 30-Martian day (31-Earth day), which was completed on May 7, 2021.
Main article: All you need to know about the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter
Celebration of 50 flights
The Ingenuity Mars helicopter has completed 50 flights as of April 13, 2023
Milestones
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter has achieved following milestones during flight:
| Date | Flight no. | Milestone | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| December 20, 2023 | 69 | Maximum horizontal distance covered | 705 m (2315 ft) |
| October 12, 2023 | 62 | Maximum flight speed reached | 10 m/s (22.4 mph) |
| October 5, 2023 | 61 | Highest altitude reached | 24 m (79 ft) |
| August 16, 2021 | 12 | Maximum flight duration | 169.5 seconds |
Please follow us on Facebook and Twitter to get latest space news, upcoming skywatching events and astronomy-related content.